Spine Surgery
Micro-Discectomy
Removal of the Disc
Interbody Fusion
Fusing abnormal Vertebra
ACDF
Disc Surgery of the Neck
Neck Corpectomy
Vertebral Surgery of the Neck
Thorasic Corpectomy (Back)
Vertebral Surgery of the Back
Vertebroplasty
Cement Injection for Fractures
Kyphoplasty
Balloon inflation of Collapsed vertebra
Scoliosis Surgery
Scoliosis Deformity Correction
Endoscopic Surgery
Pen-hole, Key-hole Surgery
Micro-Discectomy
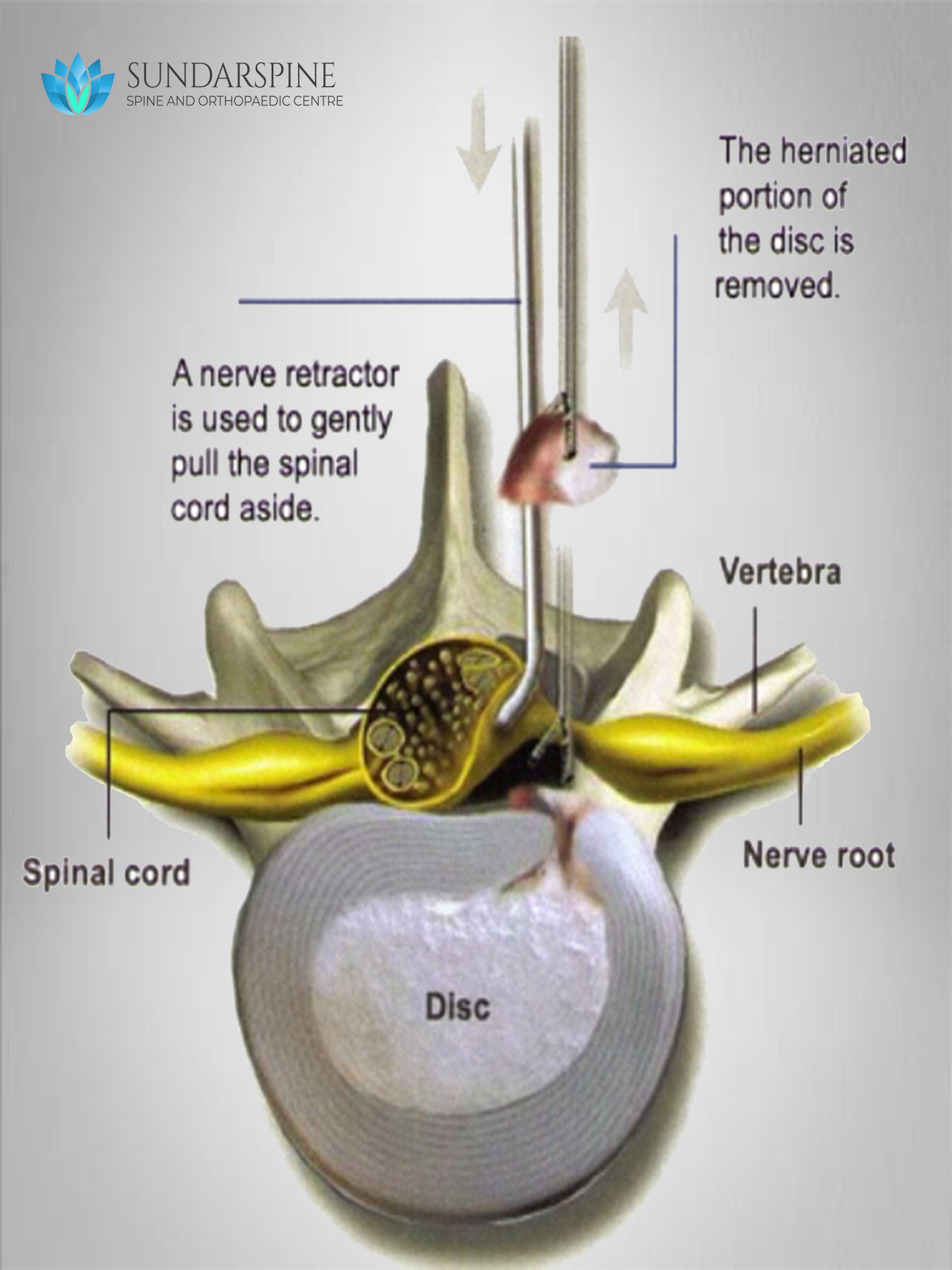
Spinal surgery once meant large incisions, long recovery periods, and painful rehab. Fortunately, surgical advances like the microdiscectomy procedure have improved the process.
Microdiscectomy, also sometimes called microdecompression or microdiskectomy, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed on patients with a herniated lumbar disc.
During this surgery, a surgeon will remove portions of the herniated disc to relieve pressure on the spinal nerve column.
The goal of a microdiscectomy is to remove the disc material placing pressure on the nerves.
The procedure is done under general anesthesia. You will be unconscious during the entire procedure and unable to feel anything. The procedure is performed with the patient lying face down. The process goes as follows:
- A 1- to 1 1/2-inch incision will be made directly over the affected disc.
- A lighted microscope is used to help your surgeon see the affected area.
- The surgeon may remove a small portion of bone that protects the root nerve.
- With a scissor-like tool, your surgeon will remove the damaged herniated tissue, relieving the pressure on the nerve.
- The incision is closed with sutures.
- The patient is usually discharged the same day or the next morning.
The spinal nerve now has the space it needs inside the spinal column, so any pain caused by pinching on the nerve should stop.
Brace (Lumbar): 1-2 weeks
Interbody fusion
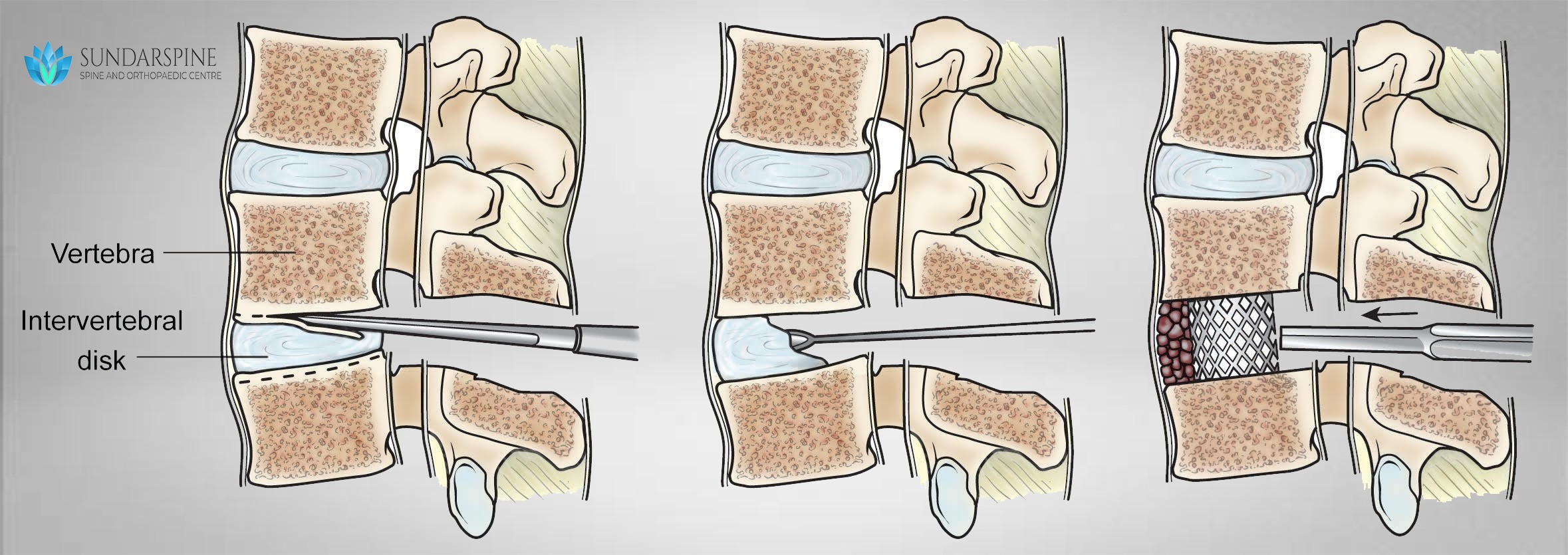
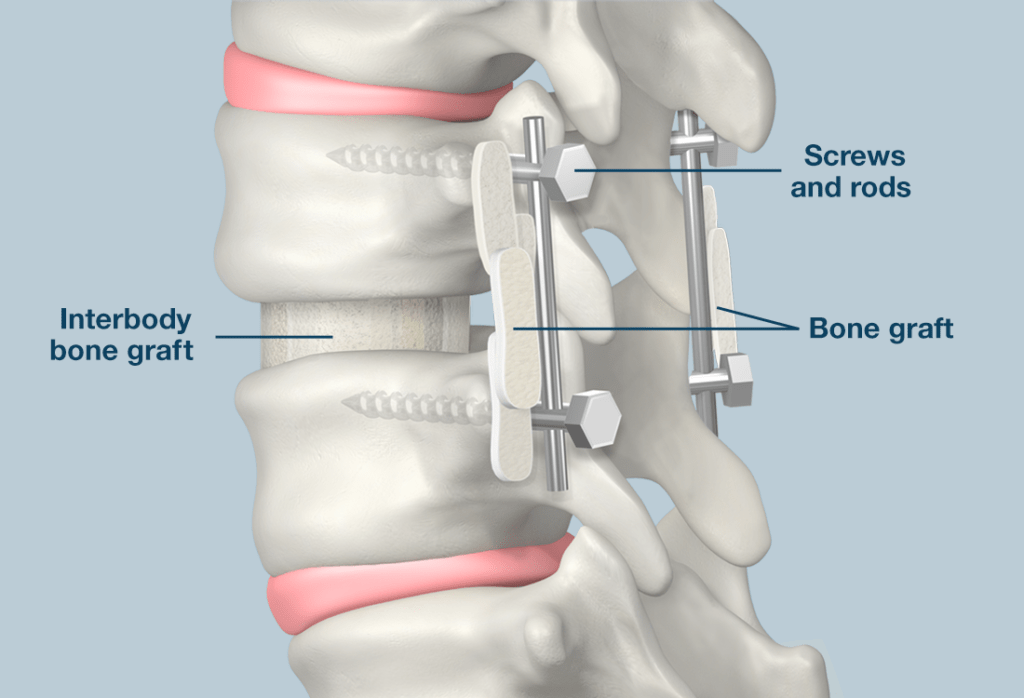
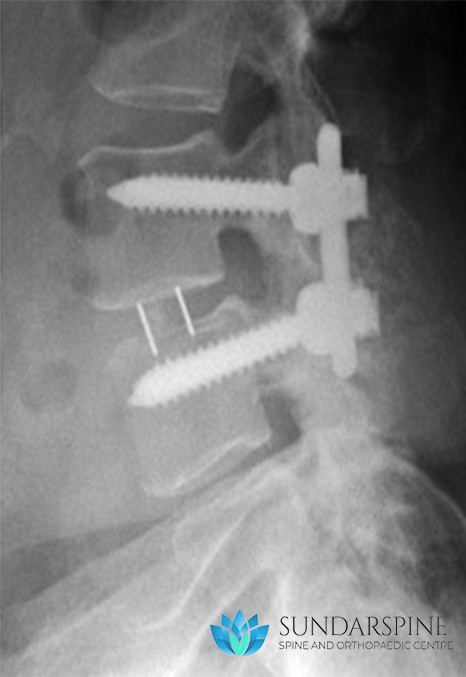
Spinal fusion (such as a TLIF) is a surgical technique to stabilize the spinal vertebra and the disc or shock absorber between the vertebra. Lumbar fusion surgery is designed to create solid bone between the adjoining vertebra, eliminating any movement between the bones. The goal of the surgery is to reduce pain and nerve irritation.
Spinal fusion may be recommended for conditions such as spondylolisthesis, degenerative disc disease or recurrent disc herniations. Surgeons perform lumbar fusion using several techniques such as TLIF (Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion) and PLIF (Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion).
How the surgery is performed?
TLIF back surgery is done through the posterior (back) part of the spine.
- Surgical hardware is applied to the spine to help enhance the fusion rate. Pedicle screws and rods are attached to the back of the vertebra and an interbody fusion spacer is inserted into the disc space from one side of the spine.
- Bone graft is placed into the interbody space and alongside the back of the vertebra to be fused. Bone graft is obtained from the patient’s pelvis, although bone graft substitutes are also sometimes used.
- As the bone graft heals, it fuses the vertebra above and below and forms one long bone.
The spinal fusion enhances the stability of the vertebral segment preventing/treating instability and thereby avoiding nerve root compression and painful symptoms.
Brace (Lumbar): 3-4weeks
ACDF
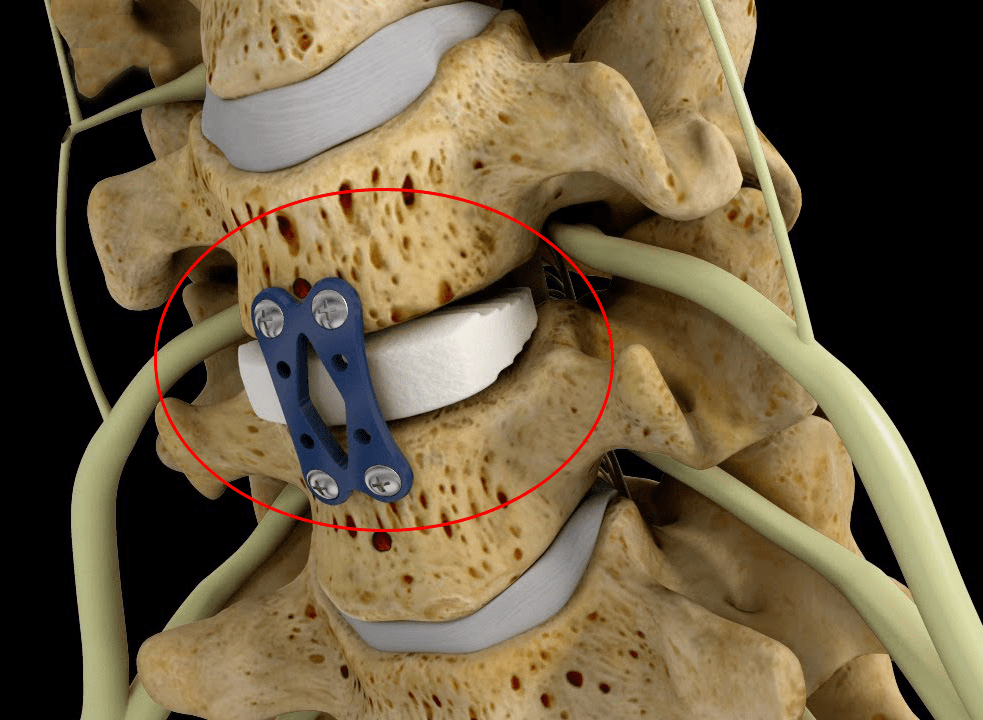
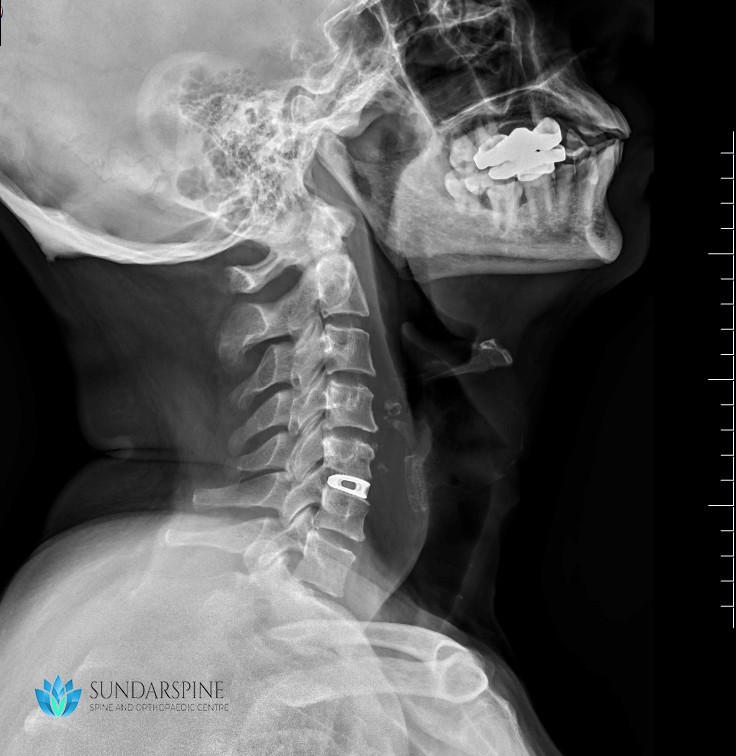
Anterior Neck discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a type of neck surgery that involves removing a damaged disc to relieve spinal cord or nerve root pressure and alleviate corresponding pain, weakness, numbness, and tingling. A discectomy is a form of surgical decompression, so the procedure may also be called an anterior cervical decompression.
An ACDF is done with an anterior approach, which means that the surgery is done through the front of the neck as opposed to through the back of the neck.
- The surgery is performed under general anasthesia.
- A 5-8 cm incision made in front of your neck, exactly over the level of disc involved.
- Muscles, trachea, esophagus and blood vessels will be retracted and the disc level will be approached.
- Disc removed entirely and end plates prepared.
- A titanium cervical cage implant will be placed with bone grafts (obtained in site) will be placed.
- Plates may or may not be used.
Advantages of ACDF:
This approach has several typical advantages:
- Direct access to the disc
- Less postoperative pain
- Less Blood loss
- Faster recovery
- Almost no surgical scar
Neck Corpectomy
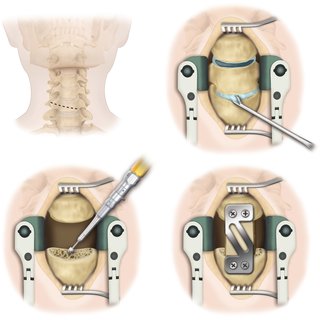

An anterior neck corpectomy is a procedure that removes damaged vertebrae and intervertebral discs from the spine in the neck, using a surgical approach through the front of the neck. This is usually done to decompress the cervical canal when the neck disease encompasses more than the disc space.
This procedure, a neck corpectomy, is often done for multi-level neck stenosis with spinal cord compression caused by bone spur (osteophytes) growth.
- The surgery is performed under general anasthesia.
- A 6-10 cm incision (Longer than ACDF) made in front of your neck, exactly over the level of disc involved.
- Muscles, trachea, esophagus and blood vessels will be retracted and the disc level will be approached.
- Both the Discs are removed entirely followed by the removal of the involved vertebra.
- A titanium neck mesh cage implant loaded with bone grafts (obtained in site) or a strut graft will be placed and fixed with plate.
Recovery time:
Thorasic Corpectomy (Back)
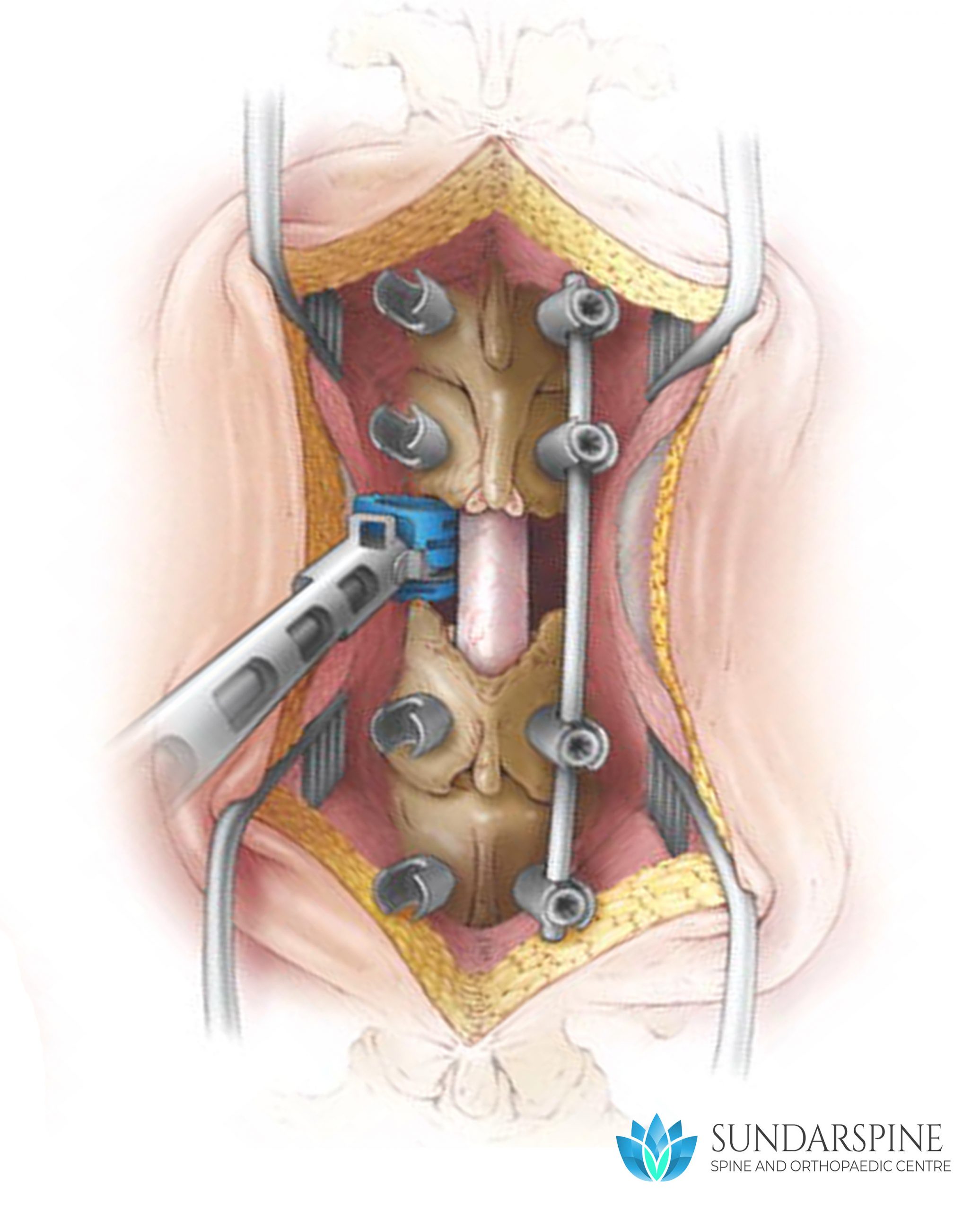
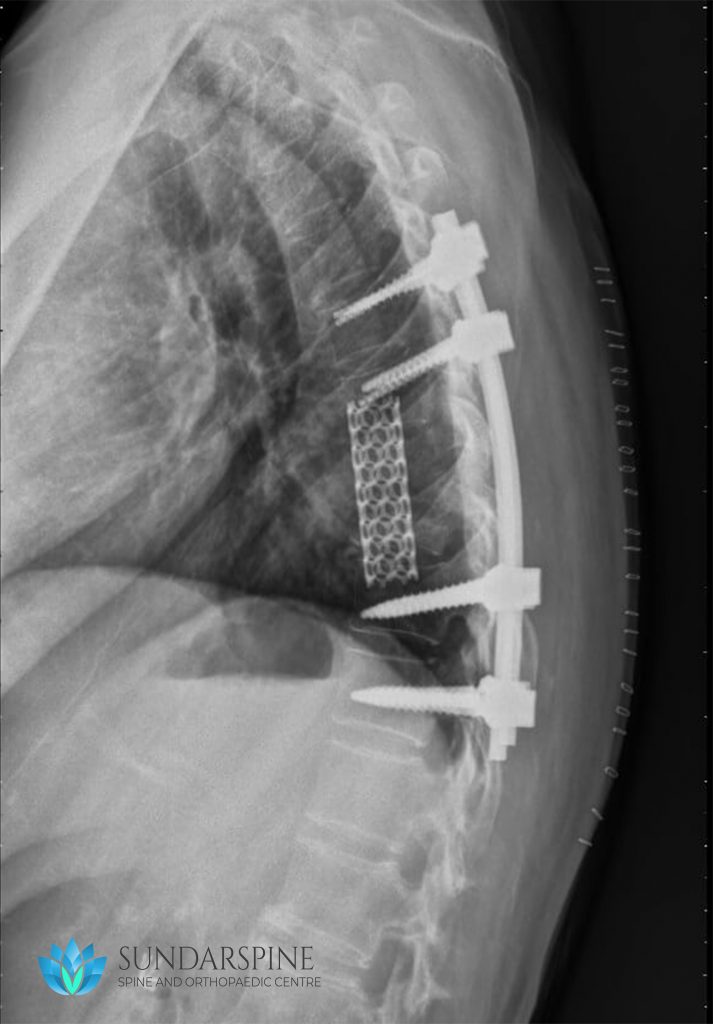
A thoracic corpectomy removes damaged vertebrae (bones of the spine) and intervertebral discs (the “cushions” between vertebrae) in the thoracic spine (spine in the upper or middle back).
Thoracic corpectomy is usually performed for patients with trauma, tumor, infection, or degenerative disease in the thoracic spine. These conditions can compress (put pressure on) the spinal cord and the nerves that exit the spine. Compression can irritate and injure these tissues. In the spinal cord, compression can cause permanent damage.
When the surgery is performed?
Tuberculosis spine, kyphosis deformity, vertebral collapse, tumour spine
- The surgery is performed under general anasthesia.
- Surgical incision may be placed in the back or front depending on the vertebra level, severity and surgeons preference.
- The vertebra and adjacent discs may be completely removed and a long mesh cage or strut graft placed.
- The construct is stabilised by screws and rods (extended multi level fixation may be required).
Recovery time:
Vertebroplasty
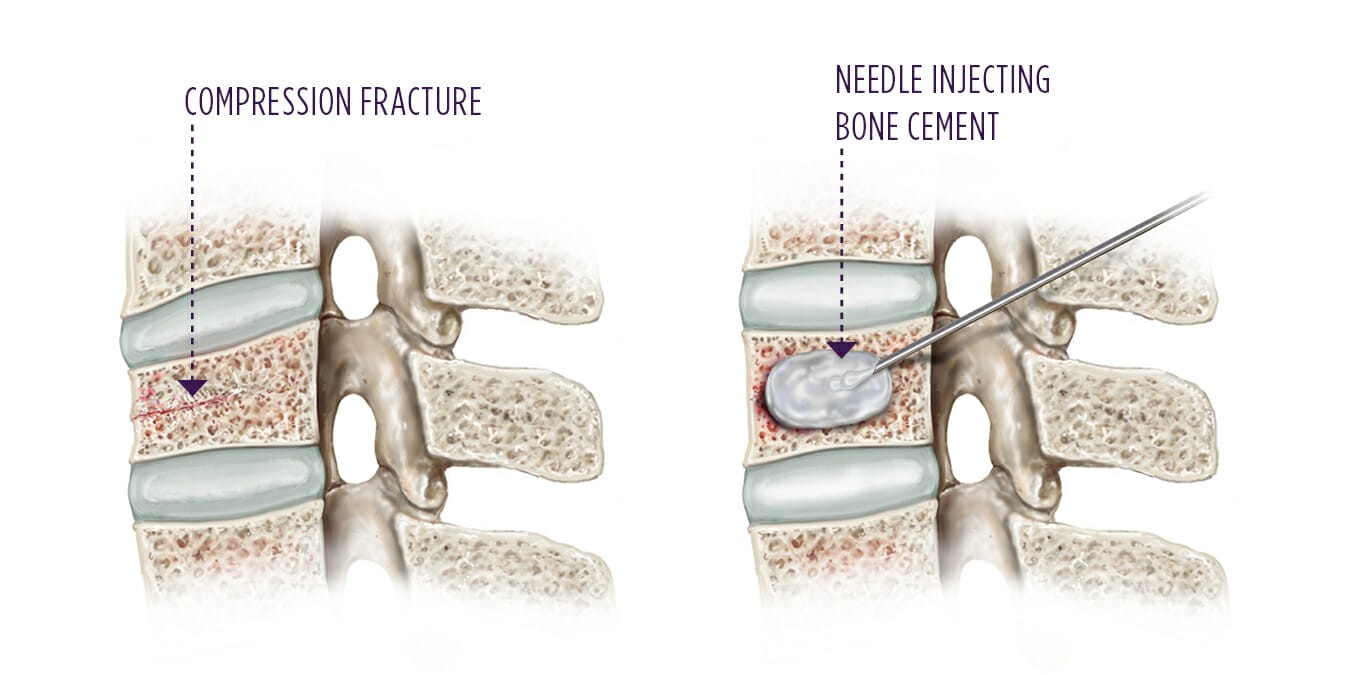
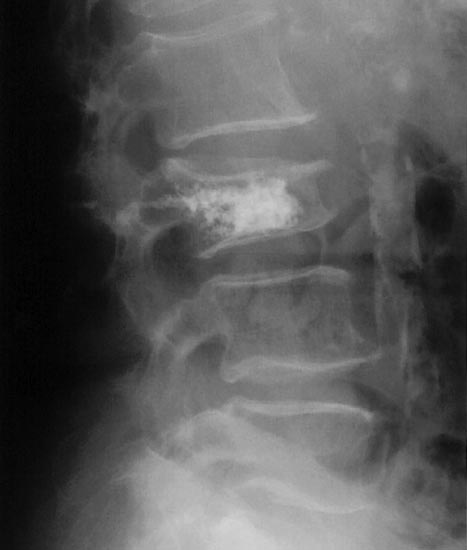
Vertebroplasty is an outpatient procedure for stabilizing compression fractures in the spine. Bone cement is injected into back bones (vertebrae) that have cracked or broken, often because of osteoporosis. The cement hardens, stabilizing the fractures and supporting your spine.
For people with severe, disabling pain caused by a compression fracture, vertebroplasty can relieve pain, increase mobility and reduce the use of pain medication.
When the surgery is performed?
Osteoporotic fracture (more than 60% collapse)
- The procedure is usually performed in local anasthesia with mild sedation.
- The vertebral level is marked using a C-arm (xray machine).
- Two bone biopsy needles are inserted on either side of the midline through the pedicles of the involed vertebra till it reached the far side of the vertebra.
- Bone cement is injected into both the needles and systematically withdrawn such that much of the vertebra is covered by the cement.
- Care is take that bone cement does not spill out of focus area especially posteriorly into the spinal canal.
- The needles are withdrawn and the needle entry site are closed by bandages without any sutures.
Recovery time:
Kyphoplasty
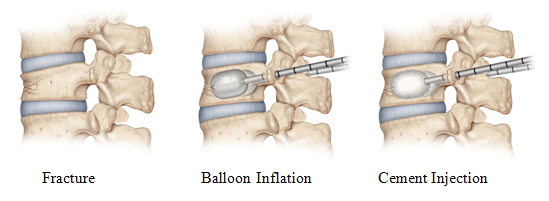
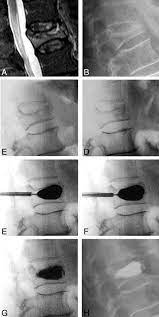
Kyphoplasty is similar to vertebroplasty, but uses special balloons to create spaces within the vertebra that are then filled with bone cement. Kyphoplasty can correct spinal deformity and restore lost height
When the surgery is performed?
Tuberculosis spine, kyphosis deformity, vertebral collapse, tumour spine
- The procedure is usually performed in local anasthesia with mild sedation.
- The vertebral level is marked using a C-arm (xray machine).
- A canula is inserted through the pedicle into the vertebral body.
- The canula is inflated like a balloon which creates a cavity in the vertebral body simultaneously correcting the kyphosis.
- Bone cement is injected through the canula such that the cavity is filled.
- Small bandage is placed to cover the entry site.
Recovery time:
Scoliosis Surgery
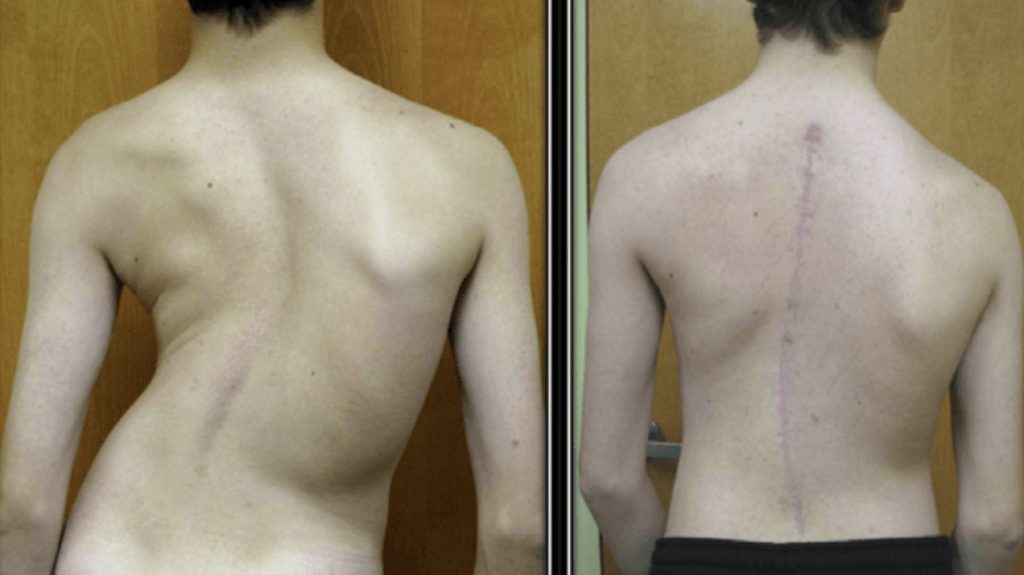
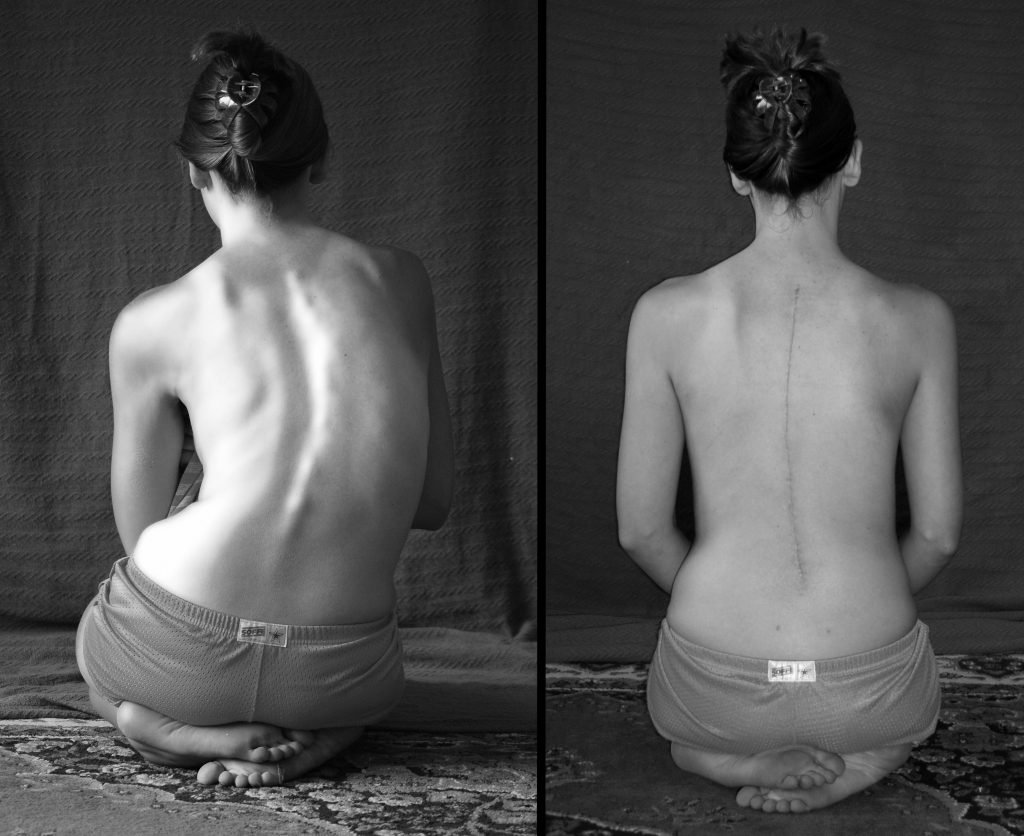
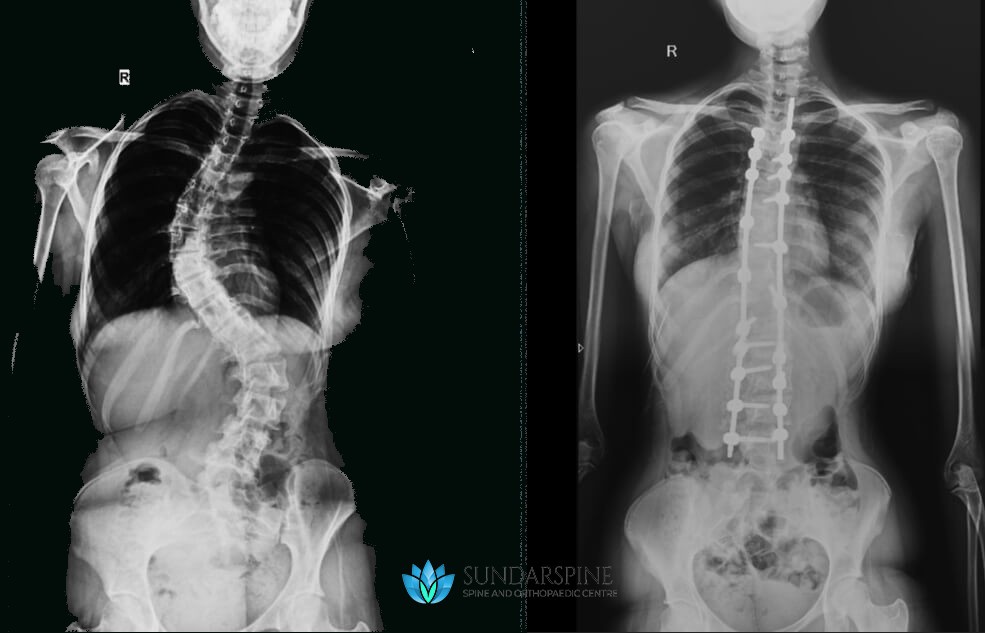
The operation for scoliosis correction is a spinal fusion. The basic idea is to realign and fuse together the curved vertebrae so that they heal into a single, solid bone.
With the tools and technology available today, scoliosis surgeons are able to improve curves significantly.
When the surgery is performed?
The decision to go ahead with scoliosis correction surgery depends on the age of the patient, severity of deformity, secondary cause, curve type and curve progression. However, most scoliosis surgeons agree that children who have very severe curves (45 to 50 degrees and higher) will need surgery to lessen the curve and prevent it from getting worse.
Advantages of Scoliosis Correction:
- Stop and reverse curve progression
- Prevent respiratory and cardiac complications
- Cosmetic improvement
- Prevent development of backpain
- Improve the lifestyle of the patient
- The surgeon and team perform a detailed evaluation of the patient and the curve for surgical planning. This involves multiple xrays in various bending and stretching positions.
- The procedure is performed under general anasthesia usually with Neuro monitoring.
- A long linear midline incision is placed on the back over the levels to be corrected.
- The muscles are systematically retracted and the pedicle screws (in levels preplanned) are applied.
- The lamina bone is removed and soft tissues are released which will make the spine flexible.
- A pre-bent rod is placed and methodically fixed and rotated to recreate the spine alignment. Bone grafts are placed on the sides for added fusion support.
- The wound is usually long involving multiple stitches and a big dressing.
In severe curves, an anterior surgery might also be necessary and will be performed in the same day or as a 2-stage (alternate day) procedure.
Recovery time:
Endoscopic Surgery
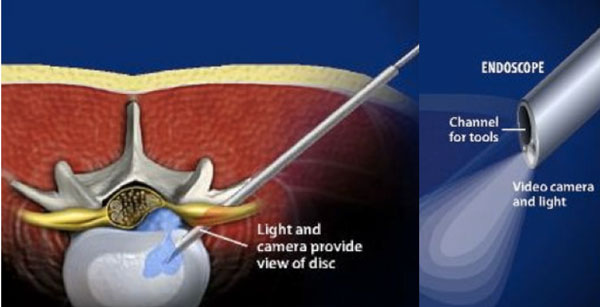
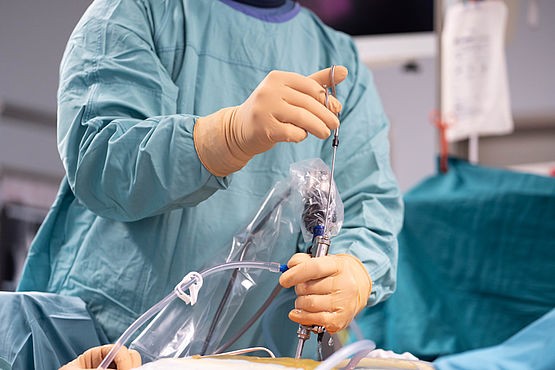
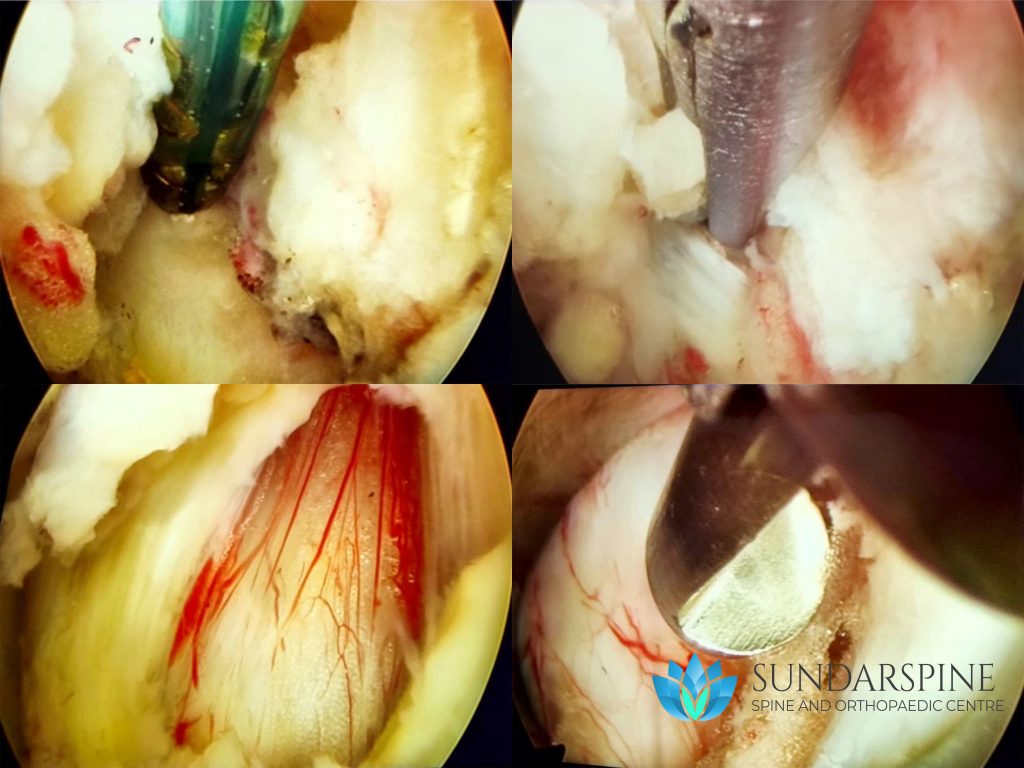
Endoscopic spine surgery is one of the latest advancement in the field of medicine. With the use of a specialized micro-camera and modern crafted instruments, many spine conditions can be treated with a portal (incision) less than 8mm in size.
When the surgery is performed?
Endoscopic spine surgery is mainly performed for Lumbar disc herniation without any significant bone spur or instability.
Advantages of Endoscopic Surgery:
- Small incision (less than 1 cm)
- Very minimal post-operative pain
- Same day discharge
- No blood loss
- Faster return to work
- No surgical scar
- The procedure can be performed under general anasthesia or with local and light sedation.
- The level of surgery is marked with the help of C-arm (xray) precisely before starting the procedure.
- A 8mm incision is made on the premarked area at the back (interlaminar approach) or at the sides (transforaminal approach)
- A dilator is used to clear a path followed by a canula and camera.
- Series of c-arm shots will be taken to confirm the camera is in correct level and position.
- A path to the diseased disc may be cleared and all the offending fragments of the disc are removed.
- Wound closed by a single suture.
Recovery time:
Spine Surgery
Surgeries of the Neck and Back
Micro-Discectomy
Removal of the Disc
Interbody Fusion
Fusing abnormal Vertebra
ACDF
Disc Surgery of the Neck
Neck Corpectomy
Vertebral Surgery of the Neck
Thorasic Corpectomy (Back)
Vertebral Surgery of the Back
Vertebroplasty
Cement Injection for Fractures
Kyphoplasty
Balloon inflation of Collapsed vertebra
Scoliosis Surgery
Scoliosis Deformity Correction
Endoscopic Surgery
Pen-hole, Key-hole Surgery
Fracture Surgery
Surgical Management of all Fractures
Plate and Screw Fixation
Fracture fixation using Plates and Screws
Intramedullary Nailing
Long rod used for Fracture fixations
Proximal Femoral Nailing
Rod fixation for Hip Fractures
K-wire fixation
Thin wire Fracture fixation
External Fixation
By Pins and rods outside the body
Joint Replacements
Arthroplasty
Hip replacement
Hemiarthroplasty, Total Hip Replacement
Knee replacement
Unicondylar and Total Knee Replacement
Shoulder replacement
Hemi, Total and Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty

Our World, Our Vision
We at SUNDARSPINE, believe in our promise to the world to provide Free access Healthcare Education to everyone. This site is a result of years of Planning and Hardwork. We are dedicated to help in your patient experience and aspire to increase our network globally and include a complete database of all health related information and guidance. We have just begun and we have a long way to go. Thank you in being a part of Us!!
We’d love to hear from you
Have any questions, Checkout
Download a FREE Ebook
Subscribe to our news letter
