- drsundar@sundarspine.com
- Youtube
For Appointments, Call
+(91) 9080 9680 66
+(91) 9080 9680 66

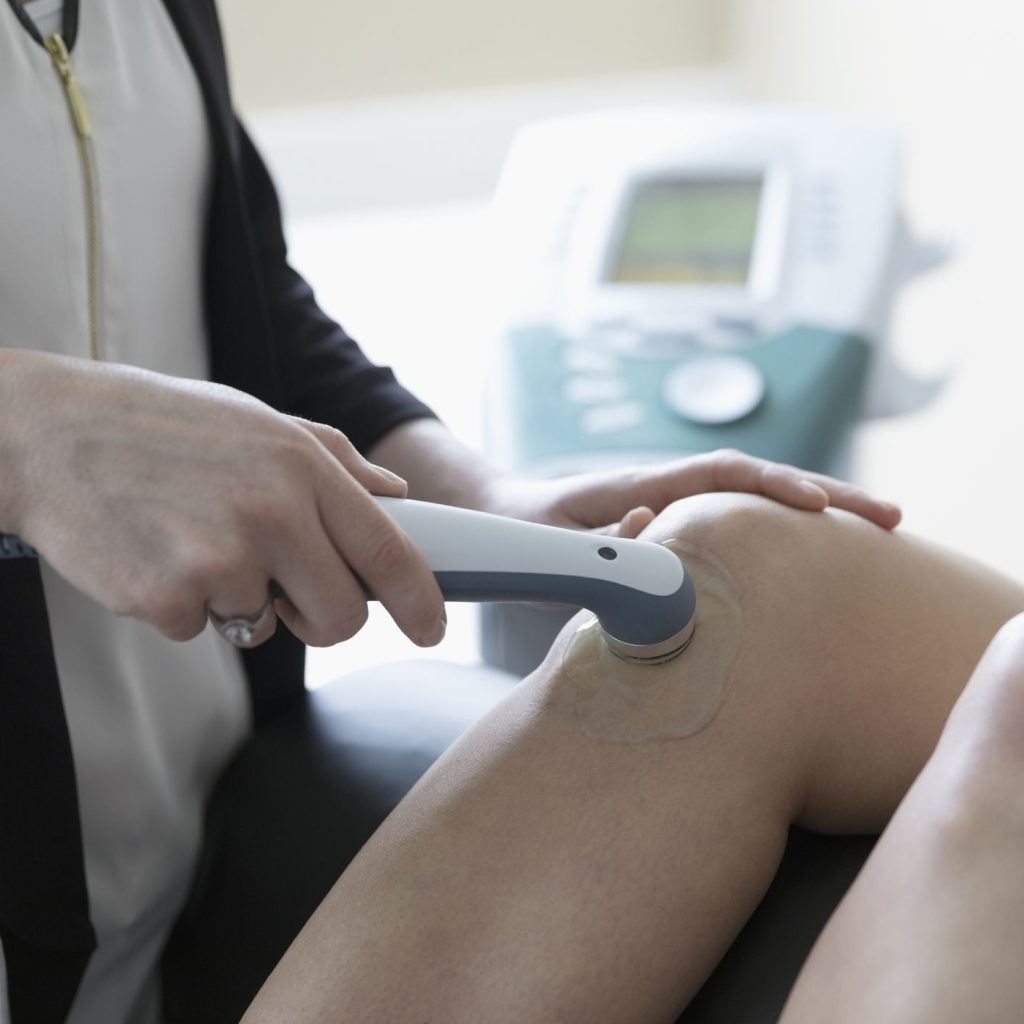
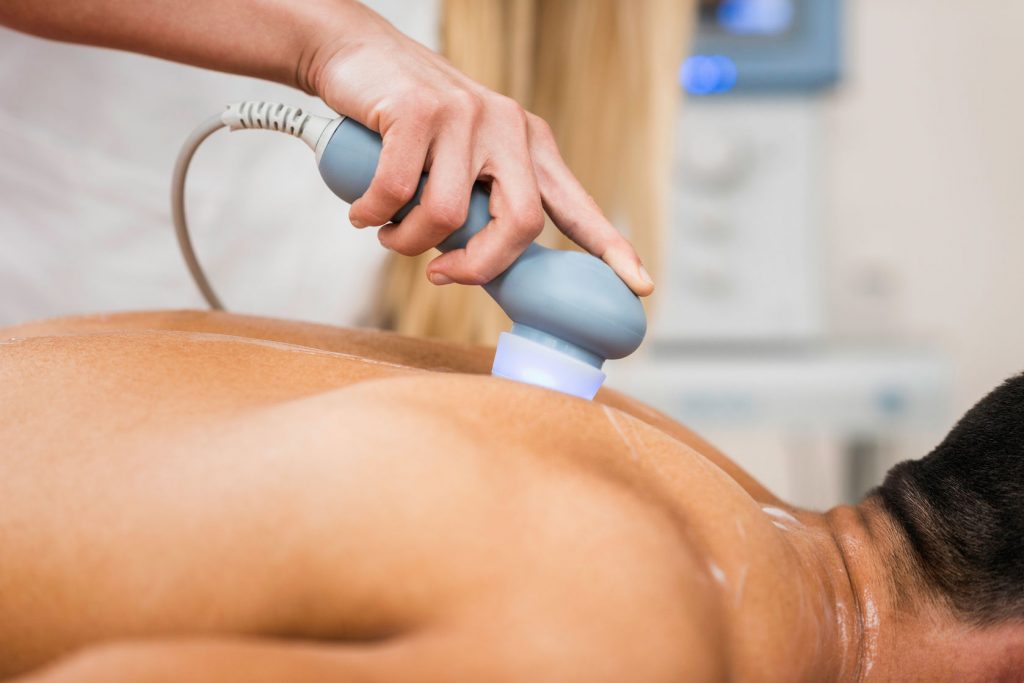
Ultrasound therapy is a treatment used by physical therapists or occupational therapists to relieve pain and to promote tissue healing.
While ultrasound therapy is not as effective for all chronic pain conditions, it may help reduce your pain if you have any of the following:
The two main types of ultrasound therapy are thermal and mechanical. Both use sound waves generated by a transducer head (which looks a bit like a microphone) to penetrate soft tissues.
The type of ultrasound therapy you get depends on your condition. For myofascial pain, strains, or sprains, thermal ultrasound therapy is typical. For scar tissue or swelling, like with carpal tunnel syndrome, mechanical ultrasound may work better.
How Ultrasound Therapy Is Performed
When you go in for ultrasound therapy, your therapist will select a small surface area to work on for anywhere from five to 10 minutes.
During your ultrasound therapy treatment, your therapist will continually move the transducer head over and around the selected area.
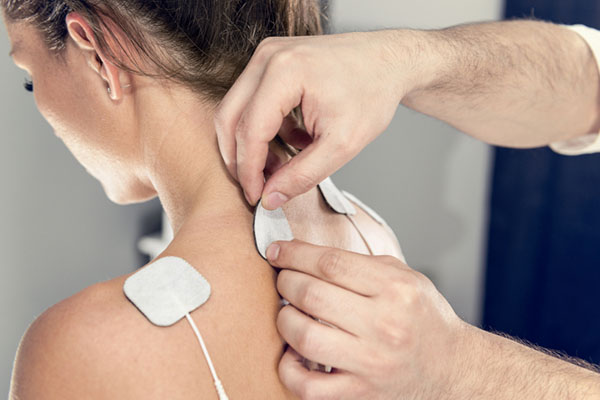
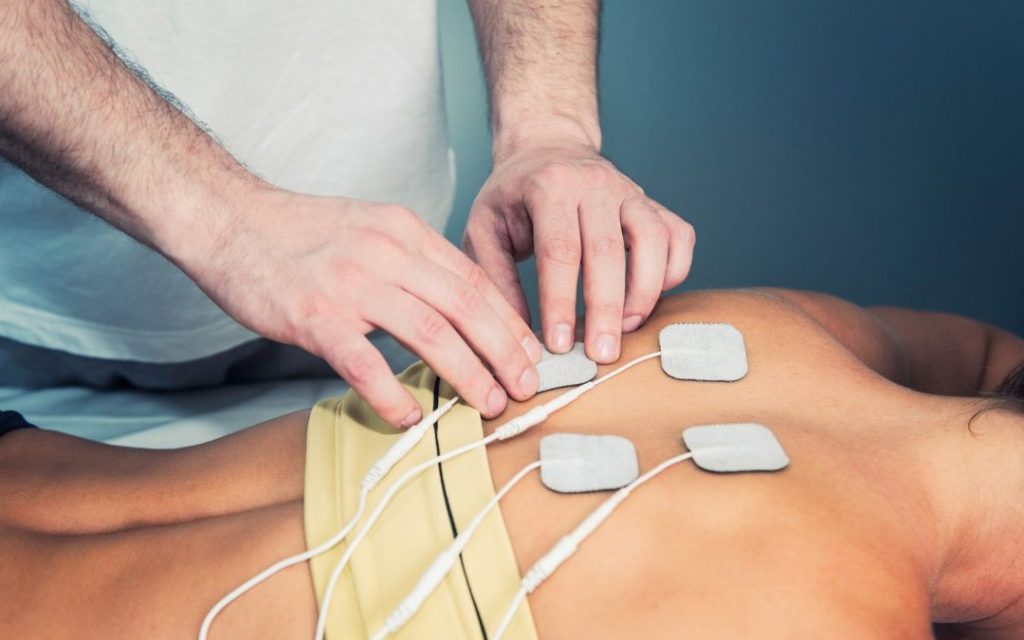
Interferential Therapy (IFT in short), is a highly recommended and practiced therapy by physiotherapists and pain specialists for treating muscle spasms and strains since many years now. It is a drug-free, non-invasive promotion of healing and pain relief which now comes infused in a small, portable and handy device with multiple interferential modes and other settings that is capable of delivering ‘proper’ IFT machine for physiotherapy.
IFT Physiotherapy Equipment transmits a continuous stimulation deep into the affected tissue thereby blocking the pain signals and reducing swelling and inflammation which causes pain. They also stimulate the secretion of endorphins, the body’s natural pain relievers and aid in relaxing strained muscles and promoting soft-tissue healing.
IFT works in a special way as it uses interferential rather than normal stimulation. The main clinical applications for which IFT is used are:
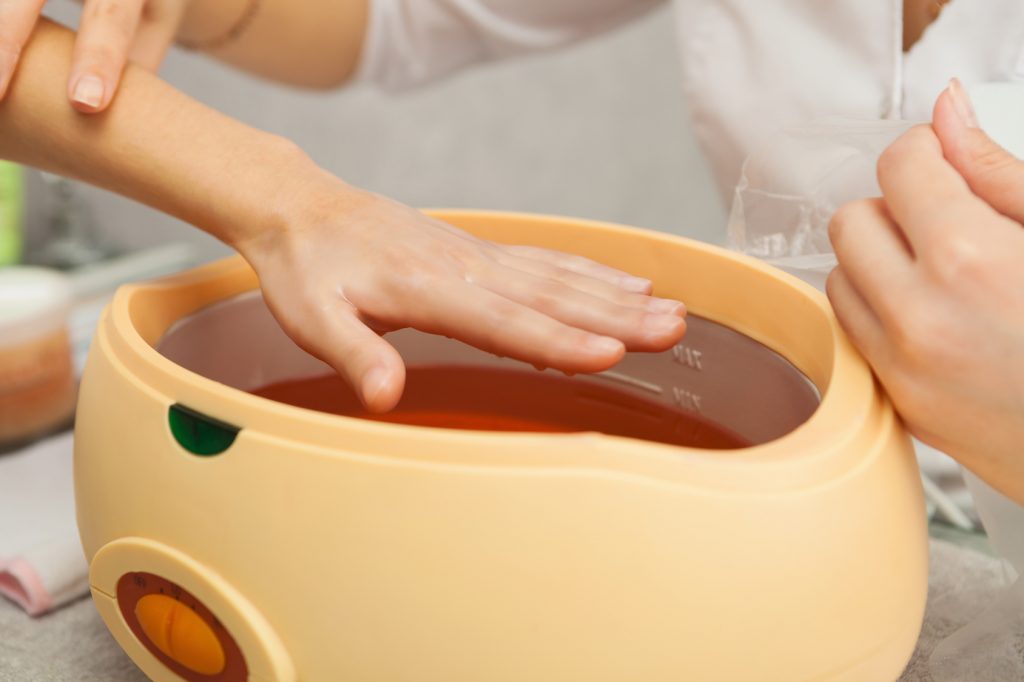
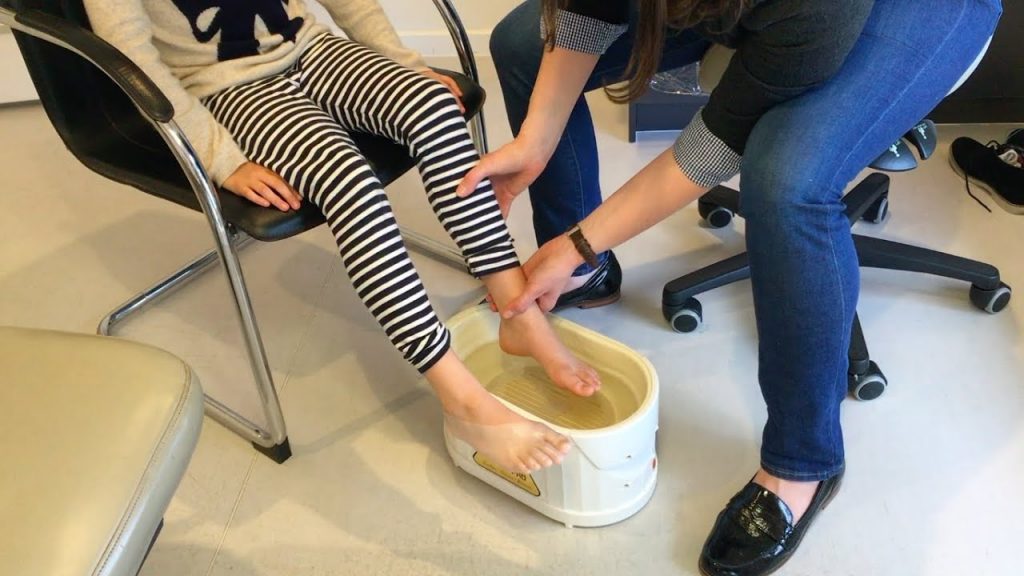
Wax therapy is a form of deep heat therapy one of the most effective ways of applying heat to improve mobility by warming the connective tissues. Wax Therapy, involves the application of molten paraffin wax, to the connecting tissues causing muscle relaxation and improves joint mobility. It is mainly used to treat Painful hands and feet. It is basically used in combination with the common mobilizing techniques and customized exercise programs to achieve better results.
Effects of Wax therapy:
Wax Therapy is a painless, relaxing, and pleasurable treatment. It soothes chronic joint pain and relaxes stiff muscles. It is used to treat the conditions like:

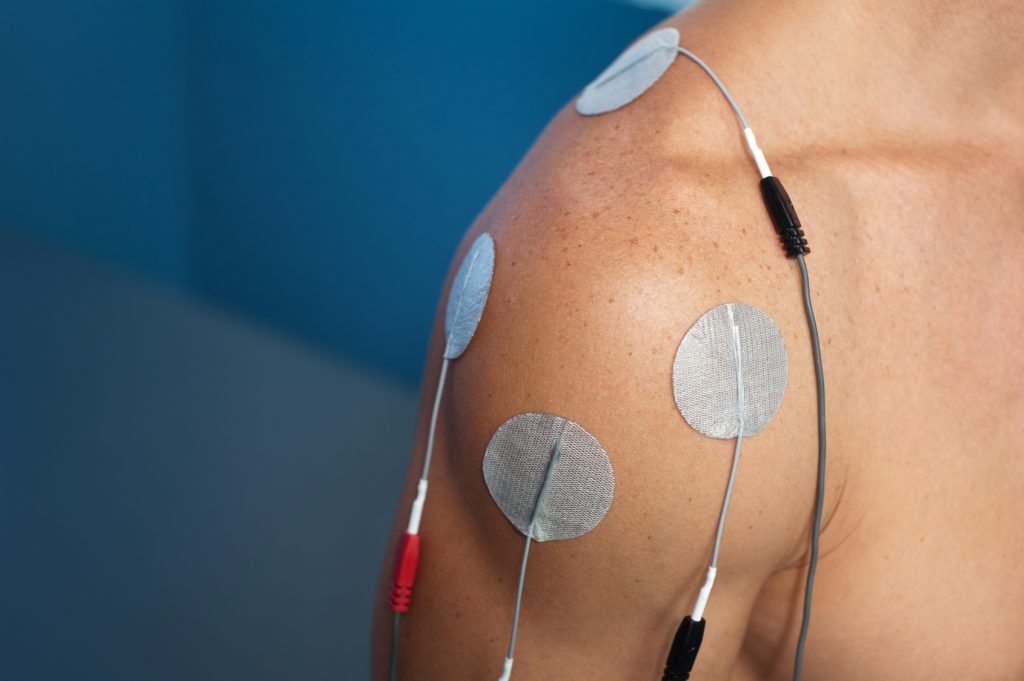
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is a therapy that uses low voltage electrical current to provide pain relief. A TENS unit consists of a battery-powered device that delivers electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the surface of your skin. The electrodes are placed at or near nerves where the pain is located or at trigger points.
How it works? The electric current stimulates nerve cells that block the transmission of pain signals, modifying your perception of pain. The nerve stimulation also raises the level of endorphins, which are the body’s natural pain-killing chemical. The endorphins then block the perception of pain.
What is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy used to treat?
TENS therapy has been used or is being studied to relieve both chronic (long lasting) and acute (short-term) pain. Some of the most common conditions for which TENS has been used include:
TENS is not safe for everyone to use. Do not use it without first getting medical advice if:
Diathermy is a therapeutic treatment most commonly prescribed for muscle and joint conditions. It uses a high-frequency electric current to stimulate heat generation within body tissues.
The heat can help with various processes, including:
Shortwave diathermy may be applied in pulsed or continuous energy waves. It has been used to treat pain from kidney stones, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
Diathermy is used to treat the following conditions:
During shortwave and microwave diathermy, two electrodes are positioned near the affected area. You must remain still while the treatment is being administered. You may feel a warm or tingling sensation during the treatment, or you may feel nothing at all.
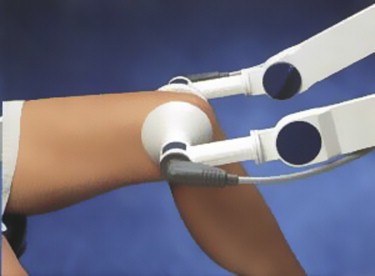

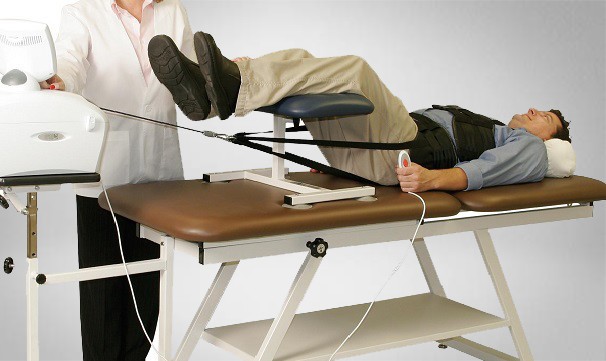
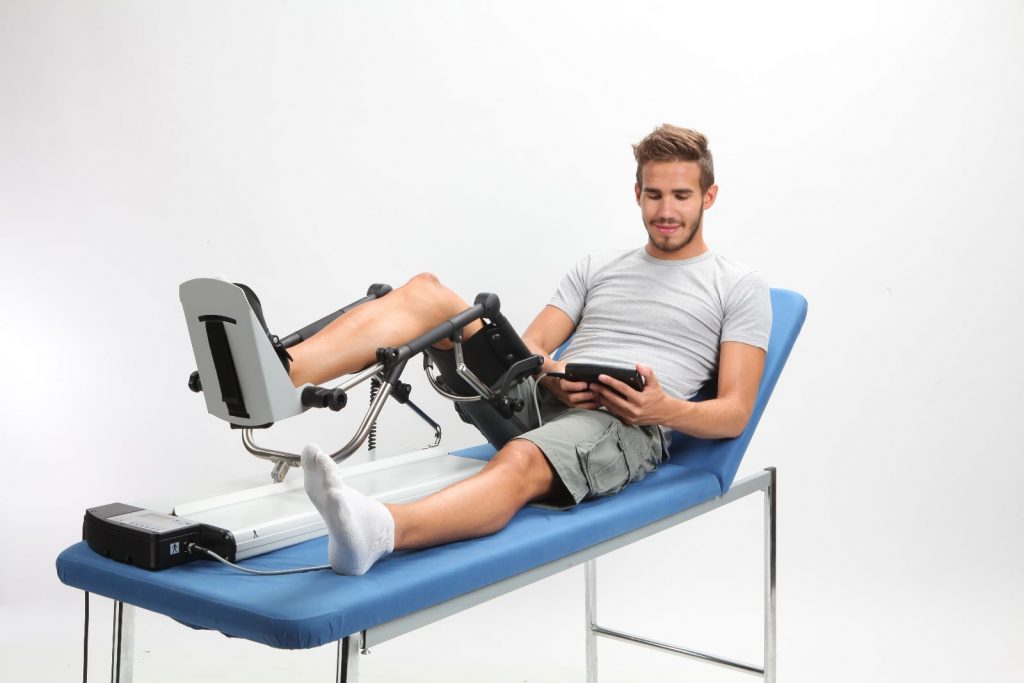
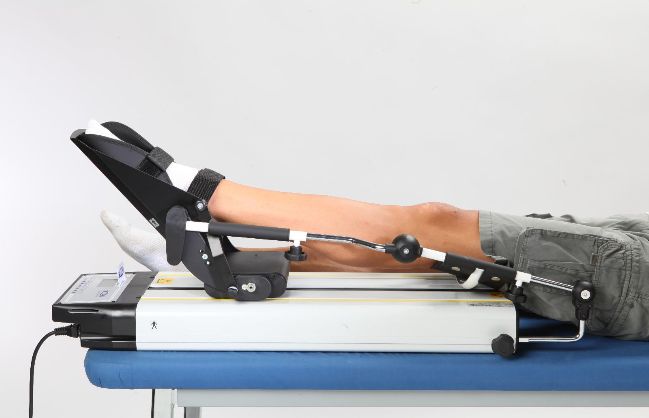
Continuous passive motion (CPM) is a therapy in which a machine is used to move a joint without the patient having to exert any effort. A motorized device gently bends the joint back and forth to a set number of degrees, and the amount of movement and speed can be adjusted by the physical therapist.
Joint stiffness after certain types of operations can be a concern. Over time, this may lead to scar tissue buildup and permanently impaired range of motion.CPM machines move your joint without you having to move your muscles. It’s thought they help by counteracting the negative effects of prolonged immobilization.
CPM machines are most commonly used on knee joints (after some types of knee surgery), but there are versions made for other joints as well.
Purpose of Therapy
Recovering normal joint mobility after surgery can be a significant challenge. The stiffness of a joint can be a complication that limits outcomes and causes pain. Because of this, some surgeons use CPM to try to prevent scar tissue formation and improve range of motion.
How it is done: For a knee CPM machine, you place your knee on the supporting frame and fit your foot into the footpad. Your leg is then secured to the machine with straps. The angle and speed used are determined by your doctor and physical therapist. You may feel pain after your procedure and are likely to be under pain medication, which will be kept in mind.
Spinal traction is a form of decompression therapy that relieves pressure on the spine. It can be performed manually or mechanically. Spinal traction is used to treat herniated discs, sciatica, degenerative disc disease, pinched nerves, and many other back conditions.
Spinal traction stretches the spine to take pressure off compressed discs. This straightens the spine and improves the body’s ability to heal itself.
It is most commonly used to treat:
Spinal traction therapy can be administered manually or mechanically, depending on your needs.
Manual spinal traction: In manual spinal traction, a physical therapist uses their hands to put people in a state of traction. Then they use manual force on the joints and muscles to widen the spaces between vertebrae.
Mechanical spinal traction: In mechanical spinal traction, you will lie on a table that has special tools to stretch the spine. A physical therapist will attach a series of ropes, slings, and pulleys to your body to mechanically relieve pressure.
Spinal traction can sometimes cause pain that is worse than the original condition. Those with osteoporosis and certain types of cancer should not use traction therapy. Spinal traction is known to cause muscle spasms and in certain cases worsen the instability.
Though spinal traction is a very popular and most common used mode of physiotherapy, some doctors dont usually prefer this technique of treatment.