- drsundar@sundarspine.com
- Youtube
For Appointments, Call
+(91) 9080 9680 66
+(91) 9080 9680 66

Advice: All the medicines stated here are for educational and informational purpose only. The diagnosis and treatment differs from person-to-person basis and can only be advised after a consult. Please do not self treat. Consult a doctor before starting any medications.
Painkillers (Analgesics) are one of the most commonly used medicines in the world that are used to treat pain. There are a large number of painkillers available and they all come in various types and different brand names. However, three main types are most commonly used:
Nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – Have a higher pain relieving activity and is associated with anti-inflammatory effect.
This is very useful to reduce pain and swelling and hence are the best drug used in injury, muscle sprains and fractures.
Opioids -They are further divided into Weak and Strong Opioids. Weak opioids are commonly used and are available as tablets in pharmacy. Strong opioids are mostly used in hospitals under observation. They have fever side effects compared to NSAIDs and hence can be used in elderly people for longer duration.


Having a muscle spasm means that one or more of your muscles is twitching or cramping out of your control. It can happen for a lot of different reasons, and can sometimes be very painful.
Muscle relaxants are the drugs that relaxes the muscle by decreasing the muscle tone and reduce muscle spasm, pain and hyperreflexia. The commonly used relaxants (spasmolytics) relieves the tension in the muscle caused due to injury or sprain thereby reducing the pain.
They are usually prescribed in combination with other pain-killers.
How they work: The muscle relaxants acts by reducing the stiffening nerve impulse from the brain which causes the muscle spasm, ultimately relaxing the muscle and reducing the pain.
The term anti-edema and anti-inflammatory are broad concept including many NSAIDs (which are primarily painkillers) and Steroids. However this section is focused on the anti-edema medicines used to reduce swelling due to injury and other causes.
These medications are usually used along with other painkillers to quickly reduce swelling which inturn relieves pain and inproves mobility.
Antibiotics are medicines that fight bacterial infections by killing the bacteria or by making it hard for the bacteria to grow and multiply. There are thousands of types of antibiotics and they help the body’s immune system to resist the infection. Most of the antibiotics functions to fight a specific type of bacteria, hence a single antibiotic cannot be used for all types of infections.
How they work: There are many groups of antibiotics and each work in particular function. But in unison, they work in affecting the structure of the bacteria cell wall or DNA making them difficult to survive.
Stomach or Gastro Protective drugs are those medications used to protect the outer layer of the stomach against the gastric acid. They are usually given when medications which causes gastric erosion are prescribed (Such as Painkillers and antibiotics).
How they work:
There are 2 types of stomach protectant drugs –
1. Acid Reducers: Protects by reducing the gastric acid secretion. (eg. Pan, Rantac)
2. Stomach-liners (Antacids): Protects by forming a protective outer layer. (Eg: Digene, gelusil)
The protective layer forming drugs affect the absorbption of certain drugs, hence acid reducers are more commonly used for this purpose.
Neurologics are drugs that reduces the abnormal stimulation of the nerves. They are used in spine and orthopaedic conditions to treat sciatica or radiating nerve pains.
How they work: The neurologics works by reducing the sensitivity of the nerves to external abnormal stimulation. When the nerve is compressed due to any causes, the pain fibres are trigerred along the pathway. The neurologics acts by reducing this stimulation thereby reducing nerve related pain.
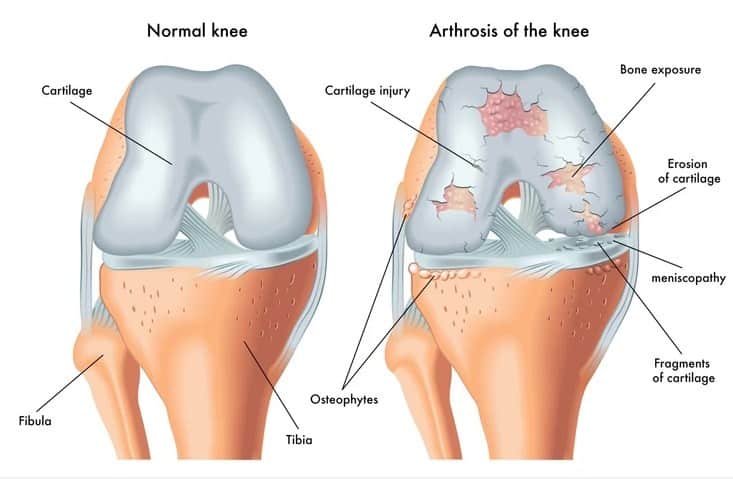
Joint Preserving drugs or Chondro-protectives are a group of drugs that works in preserving and regrowing the cartilage layer of the joints. They are used in early arthritis and in tendon inflammatory conditions. Though no confirmatory research has proven any advantages of their uses, they have been used widely all over the world. They are usually available as a 4 or 5 drug combination.
How they work: The drug works as a supplement, to replenish the damaged and used collagen and by attempting to reconstruct the cartilagenous layer. They may not work in severe arthritis as the wear and tear are so severe to compensate for any supplements.
Supplements are nutritional medications that are usually prescribed for vitamins and mineral deficiency. Vitamins and minerals are important nutritions essential for the good functioning of the body. They are available in normal diet, however, when they are deficient in it is essential to supplement with medications. They are usually available in combinations.
How they work: Supplements contain a component of the vitamins or minerals in their best absorbable property. Once taken, they get directly absorbed into the bloodstream and maintain the normal functioning of the body.

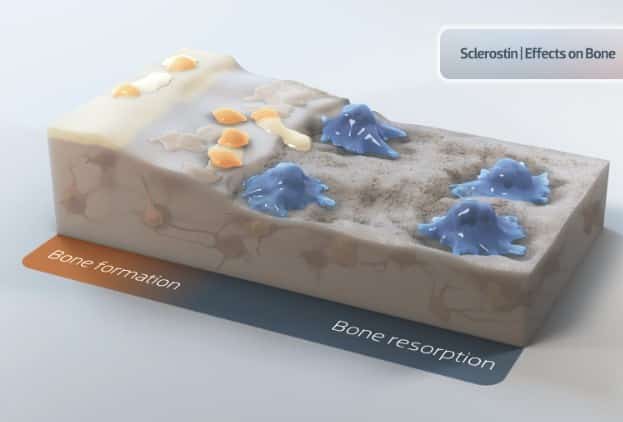
Osteoporosis is the decrease in bone density and strength resulting in bone pain and fractures. They are very common in females and in old ages thereby requiring treatment. Recent advancement in medical sciences have promoted development of many types of Osteoporotic medication which are very effective in recovering bone mass.
How they work: Osteoporosis medications work by 2 types –
They work by reducing the activity of bone resorbing cells (osteoclasts) in the body and increse the activity of the bone forming cells (Osteoblasts).

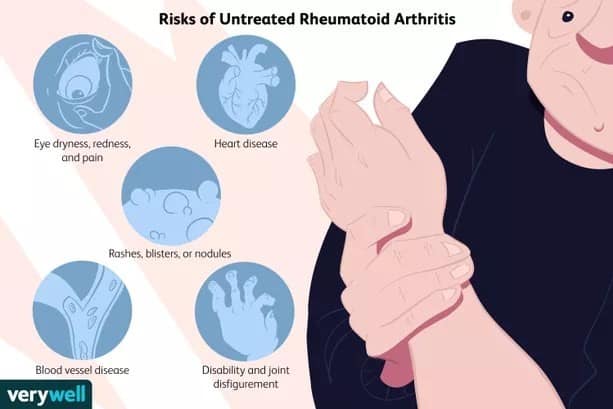
While there’s no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, physiotherapy and medication can help slow the disease’s progression. Most patients can be managed with a class of medications called anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDS). These drugs can slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and save the joints and other tissues from permanent damage.
How they work: There are many types of anti-rheumatoid drugs although their main function is to counter the immune cells that act against and damage the joints.
Ointments and Gels have been one of the major sold drugs in the orthopaedic pharmacy for pain management. They have the advantage of easy application, faster action, and with no side effects. Most of the ointments are a combination of multiple drugs and can be purchased over the counter without any prescription.
How they work: The ointment when applied penetrates the dermal layer of the skin and acts locally in reducing the pain mediators. In addition, some drugs stimulate the local sensory nerve endings and gate the pain nerves blocking their stimulus.

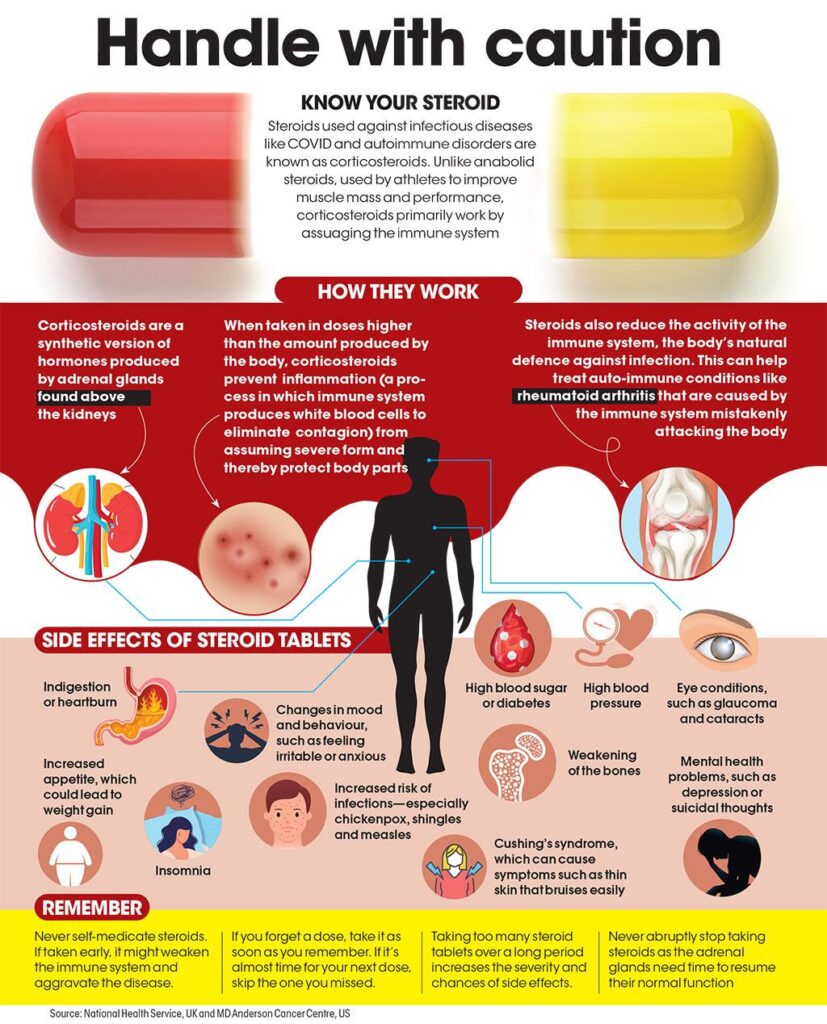
Steroids are man-made version of naturally produced hormones in the human body. They are one of the most effective and the most abused drug for pain and inflammation. Their superior action is only countered by their added side-effects due to long-term use. However, used specifically for indicated conditions, these complications can be prevented. Steroids injections have very good relief for certain subacute and chronic conditions such as early arthritis, tennis elbow and plantar fascitis.
How they work: Steroids work by reducing the inflammatory mediators which are responsible for pain and inflammation. They mimic the action of corticosteroids, a naturally occurring harmone in the body.