- drsundar@sundarspine.com
- Youtube
For Appointments, Call
+(91) 9080 9680 66
+(91) 9080 9680 66

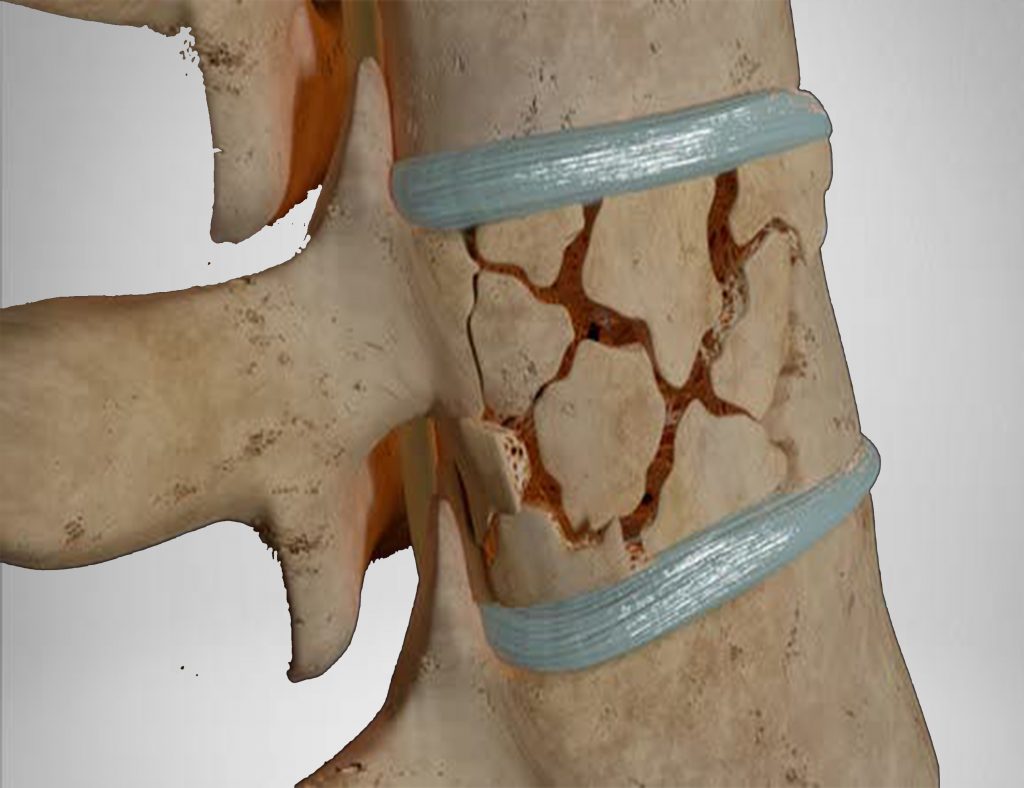
Disc Prolapse or Slipped disc is backward migration of the damaged disc content causing compression on the spinal canal or the nerve roots.
Symptoms: Back pain, Leg pain, Radiating pain, Numbness or weakness of the leg
Risk factor: Smoking, Lifting heavy weights, Obesity, Genetic
Causes: Sudden or chronic stress on the posterior aspect of the disc wall causing breakage and leaking of the disc contents. This causes compression and irritation of the nerve roots, and if significant, the cord.
When to see a Doctor: Back pain for more than a week, Severe pain, Difficulty in standing and walking, radiating pain to the legs, numbness or weakness.
Treatment: Mainly by medication, rest and exercise. Surgery only for acute or severe conditions
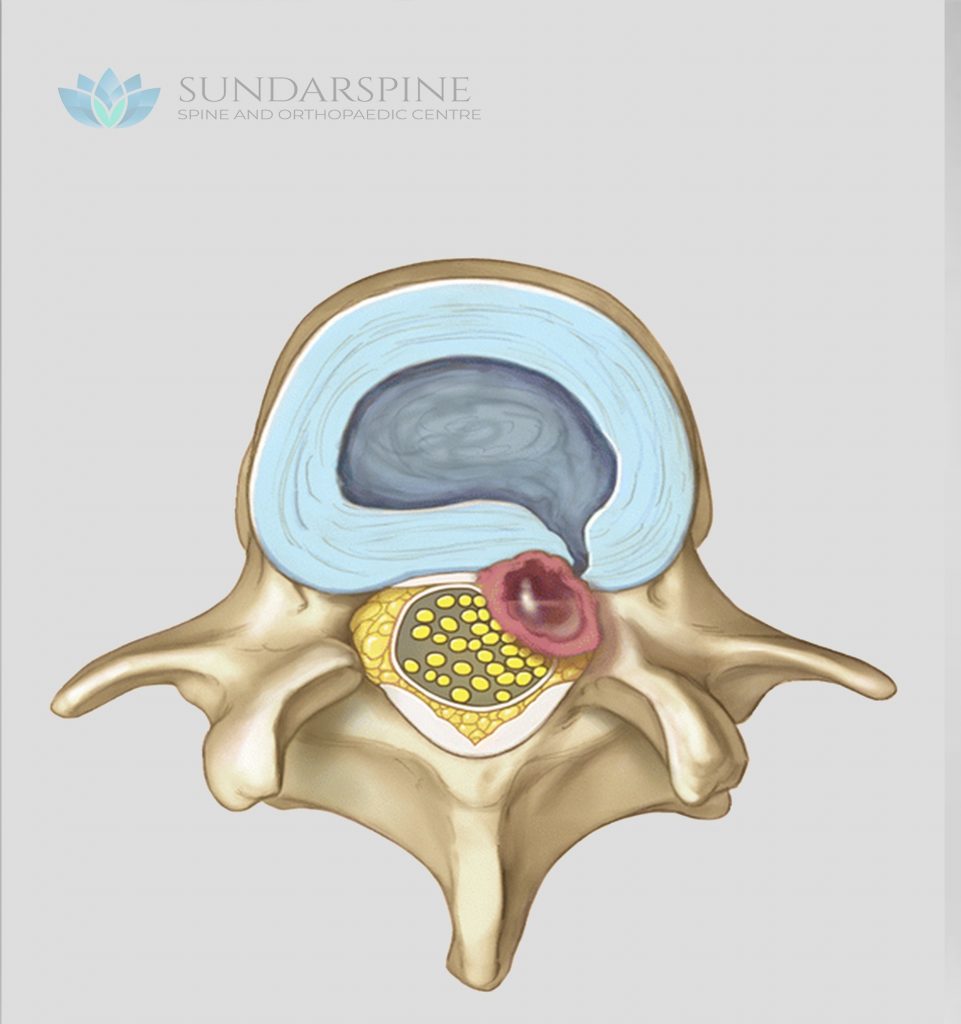
Spondylosis is a type of arthritis spurred by wear and tear to the spine. It happens when discs and joints degenerate, when bone spurs grow on the vertebrae, or both. These changes can impair the spine’s movement and affect the nerves and other functions.
Symptoms: Back pain, Pain on extension,
Treatment: Observation, medical management, or surgical management depending on the severity and chronicity of pain, presence of instability or neurological deficits.
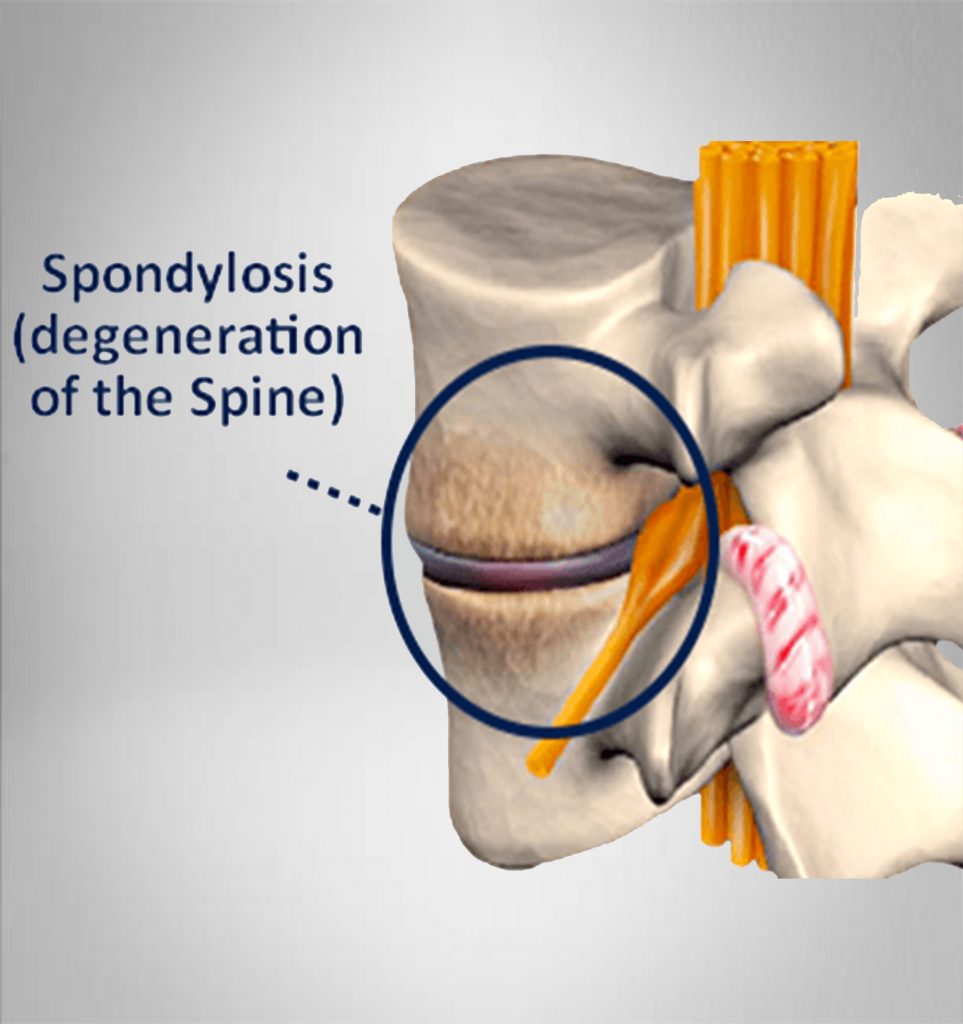
Spondylolisthesis is a spinal condition that affects the Lower vertebra (spinal bones). This disease causes one of the lower vertebrae to slip forward onto the bone directly beneath it. It’s a painful condition but treatable in most cases. Both therapeutic and surgical methods may be used. Proper exercise techniques can help you avoid this condition.
Symptoms:
Risk factor: Age, Athletics, Genetic
Causes: Overextending the spine is one of the main causes of spondylolisthesis in young athletes. Genetics may play a role, too. Some people are born with thinner vertebral bone. In older adults, wear and tear on the spine and disks (the cushions between vertebrae) can cause this condition.
When to see a Doctor: Severe back or leg pain, Back pain for more than a week, Difficulty in standing and walking for long, numbness or weakness.
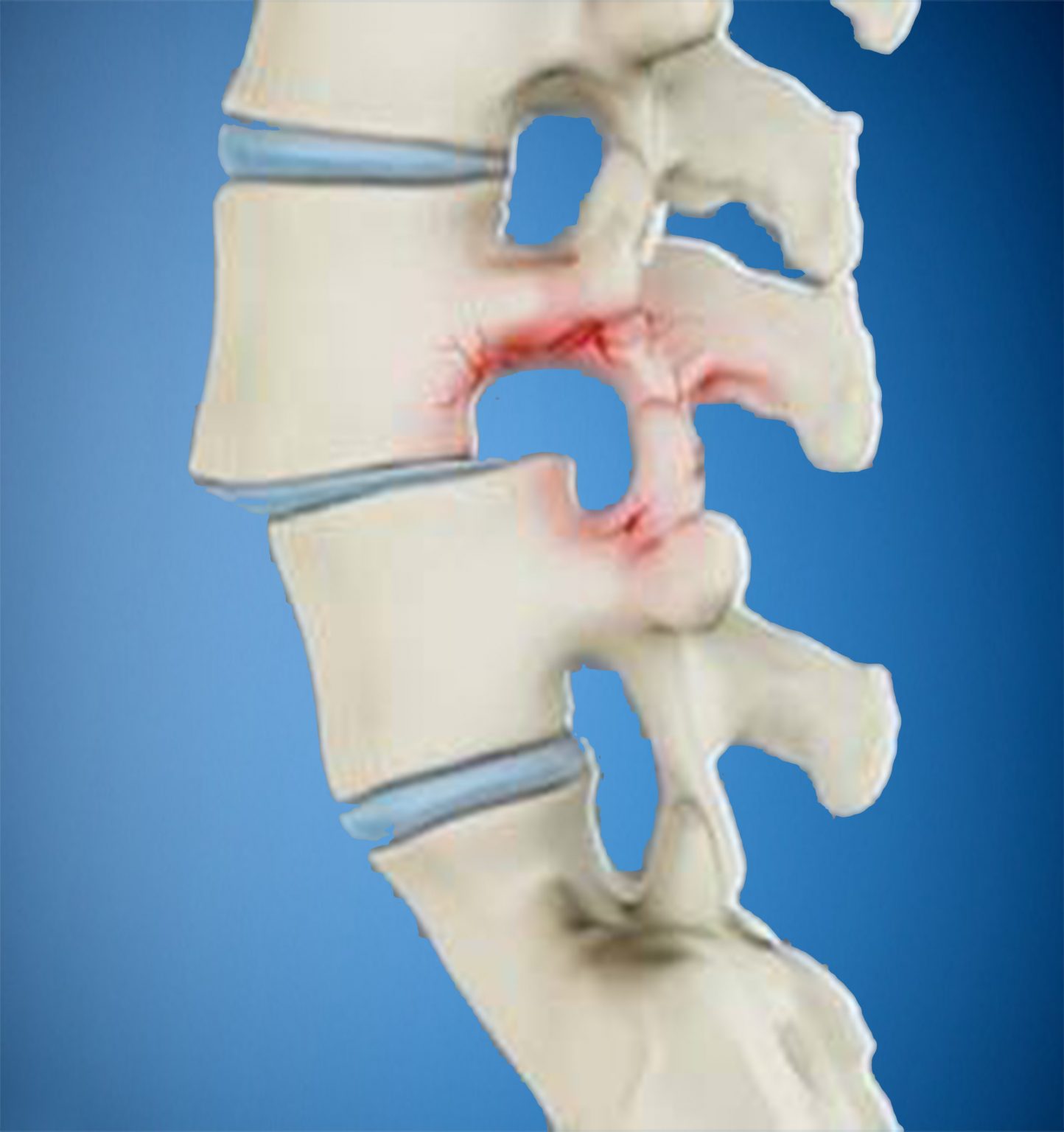
A spinal fracture is a break and/or dislocation of a vertebra in your spine. Some fractures are the result of a traumatic injury, such as a traffic accident, gunshot round or fall, and require emergency treatment. Other fractures are the result of weakened bones caused by osteoporosis.
A spinal fracture is different than a broken arm or leg, as it can cause bone fragments to pinch or damage nerves or the spinal cord.
Symptoms: Moderate to high back pain, difficulty in standing or walking, pain on lying down and getting up from bed. Severe injury with cord compression can present with numbness, weakness or paraplegia (unable to move both lower limbs)
Treatment: Stable minimal fractures without deformity can be treated with rest, brace and medications. Severe fractures with cord compression may require surgical fixation