- drsundar@sundarspine.com
- Youtube
For Appointments, Call
+(91) 9080 9680 66
+(91) 9080 9680 66

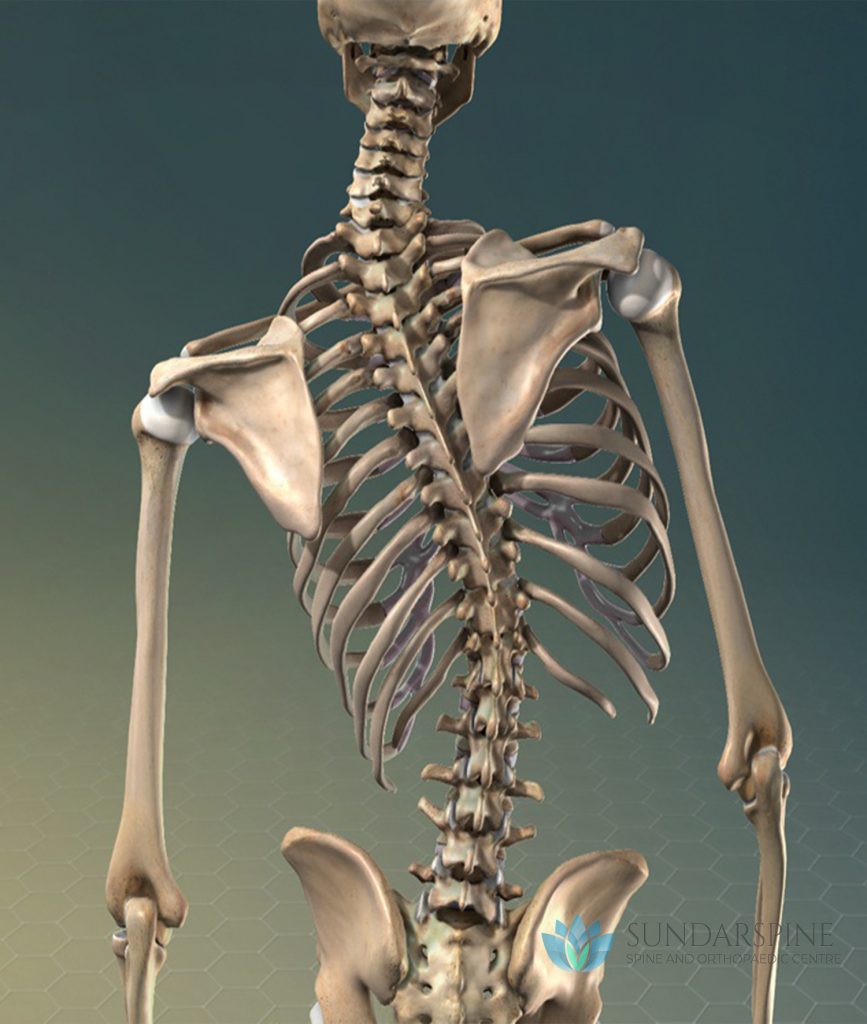
Spinal infections can be classified by the anatomical location involved: the vertebral column, intervertebral disc space, the spinal canal and adjacent soft tissues. Infection may be caused by bacteria or fungal organisms and can occur after surgery.
Tuberculosis is one of the main cause of spine infection in India.
Symptoms: Depends on the location involved – Neck or back pain, stiffness, Fever, chills, weight loss
Risk factor: Diabetes, pulmonary tuberculosis, malnutrition, tumour, long steroid use
Causes: Spinal infections can be caused by either a bacterial or a fungal infection in another part of the body that has been carried into the spine through the bloodstream.
When to see a Doctor: Immediately. Back pain in tuberculosis patient, increasing weakness or numbness.
Treatment: Mainly by medication and rest. Biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis or infecting organism. Epidural abscess or Instability risking spinal cord compromise may require surgical intervention.
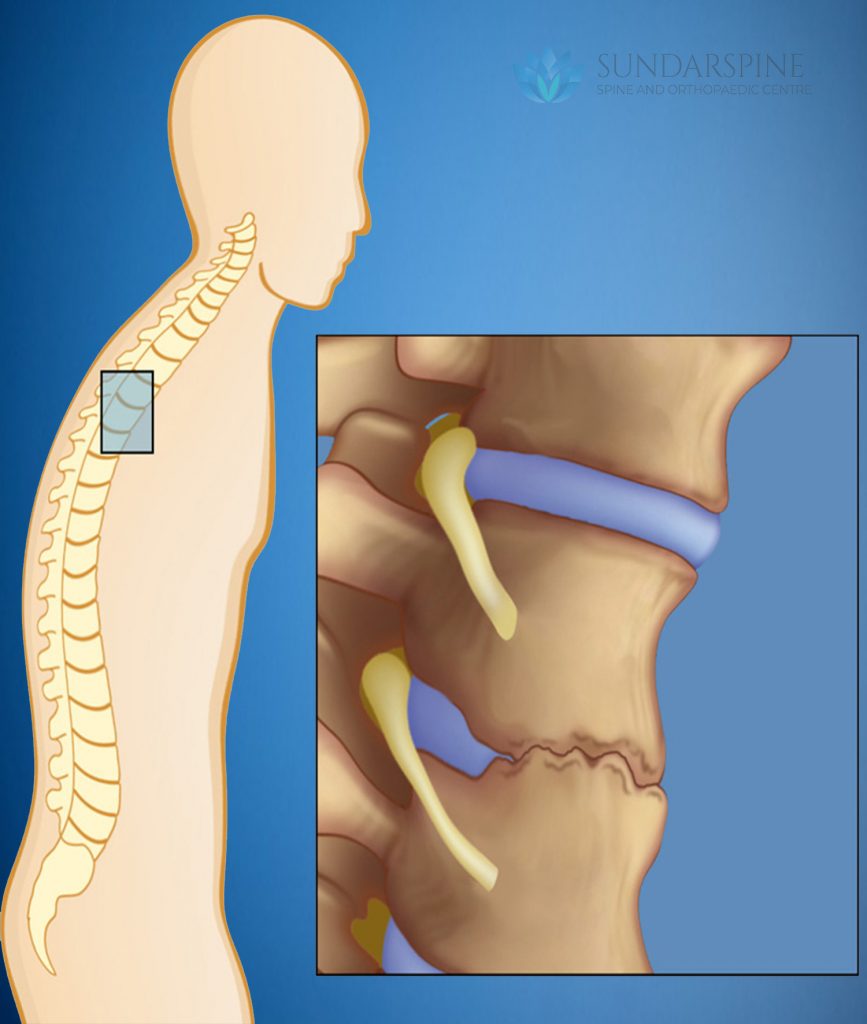
Ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammatory disease that, over time, can cause some of the bones in the spine (vertebrae) to fuse. This fusing makes the spine less flexible and can result in a hunched posture. If ribs are affected, it can be difficult to breathe deeply.
There is no complete cure for ankylosing spondylitis, but treatments can lessen symptoms and greatly slow progression of the disease.
Symptoms: Pain and stiffness especially in the early morning. Difficulty in sitting cross legged.
Treatment: Managed with medication and exercises. Medication usually has to be taken for long duration. Strictly adhering to the treatment regime may lead to good long term prognosis.
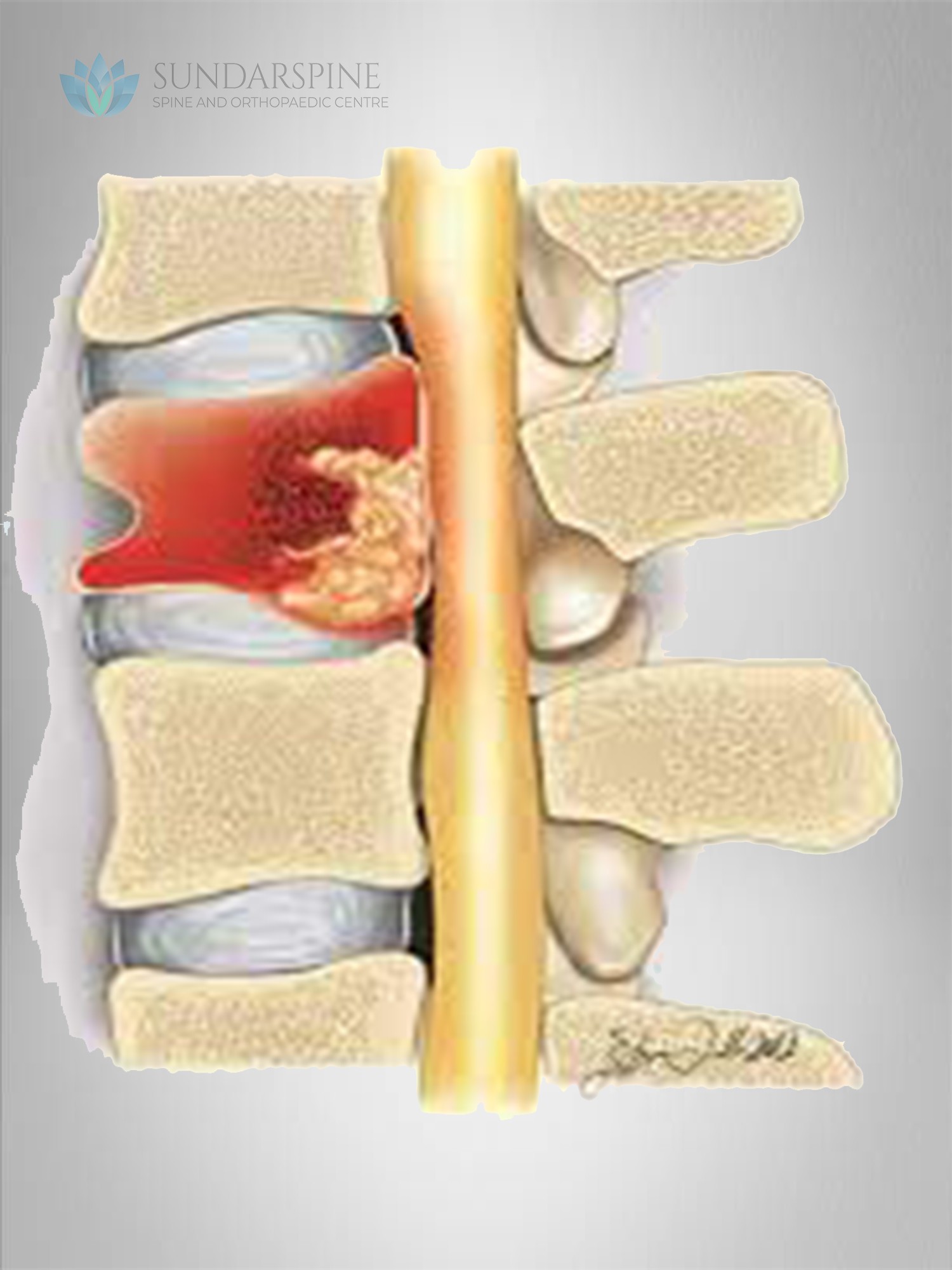
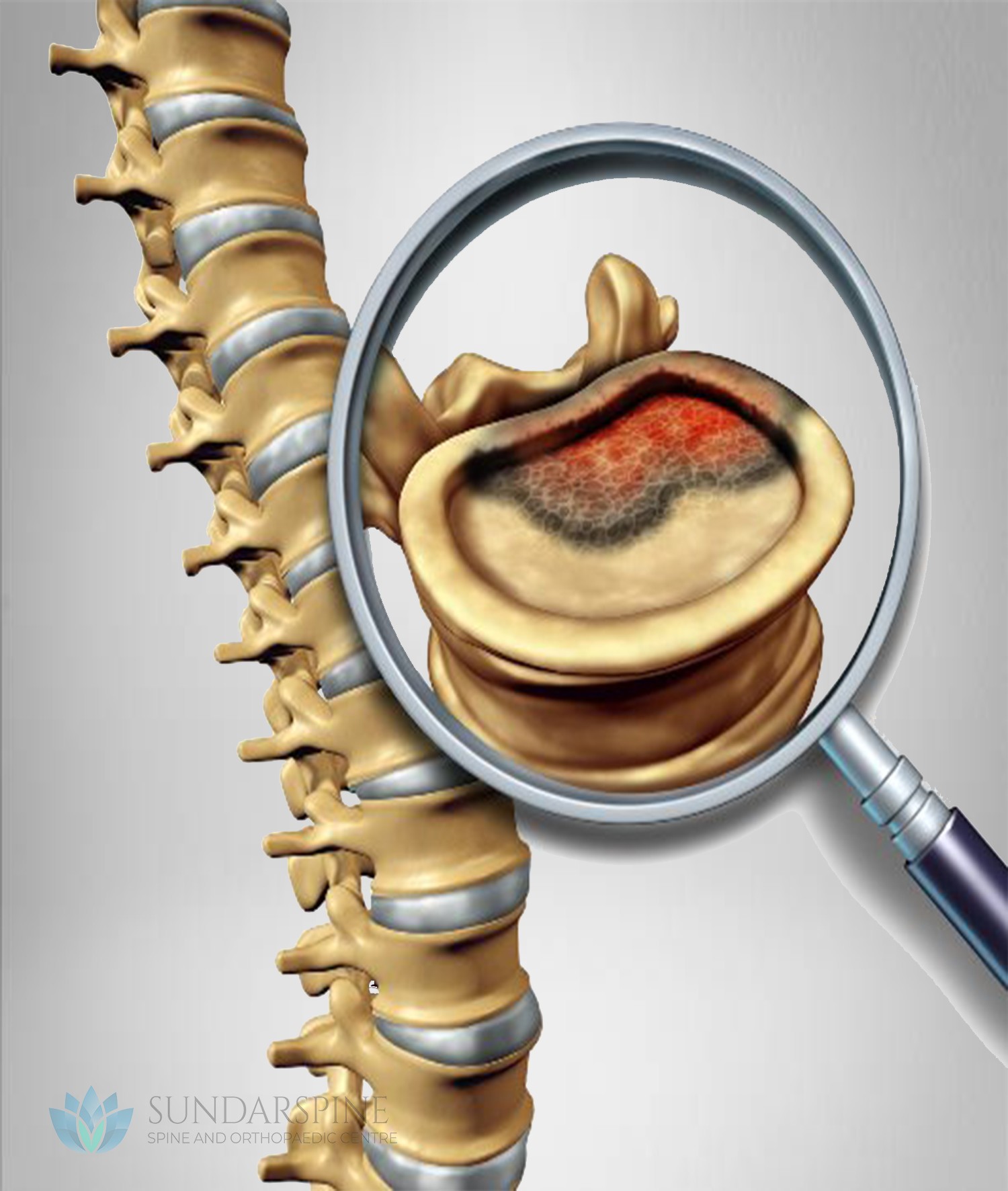
Tumors from other parts of the body can spread (metastasize) to the vertebrae, the supporting network around the spinal cord or, in rare cases, the spinal cord itself.
Spinal tumors or growths of any kind can lead to pain, neurological problems and sometimes paralysis. A spinal tumor can be life-threatening and cause permanent disability.
Symptoms:
Risk factor: Old age, rheumatoid arthritis, injury, neglected cervical disc disease
Causes: Significant compression of the cord caused due to any pathology or condition can cause myelopathy. The blood supple to the cord will be affected and result in irreversible damage unless intervened at the earliest
When to see a Doctor: Persistent and progressive back pain, not activity related, worse at night. History of cancer.
Treatment: Depends on the type of tumour. Usually biopsy may be done to confirm the diagnosis. Spinal cord compression or instability (present or impending) may require surgical intervention
Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that most often is diagnosed in adolescents. While scoliosis can occur in people with conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, the cause of most childhood scoliosis is unknown.
Most cases of scoliosis are mild, but some curves worsen as children grow. Severe scoliosis can be disabling. An especially severe spinal curve can reduce the amount of space within the chest, making it difficult for the lungs to function properly.
Symptoms:
Treatment: Mild curves are usually managed conservatively with exercises and braces. Severe curves may require major surgery.